Page 37 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 37
20 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
epoxyalcohol (24) [85] . (Note, however, that the isomeric (Z)-alkene undergoes
asymmetric epoxidation much less efficiently.) Such reactions are rendered
Ê
catalytic by the addition of 4A molecular sieves to adsorb adventitious water
which otherwise attacks the key component, the titanium tartrate complex. The
sense of asymmetric epoxidation of E-allylic primary alcohols is highly predict-
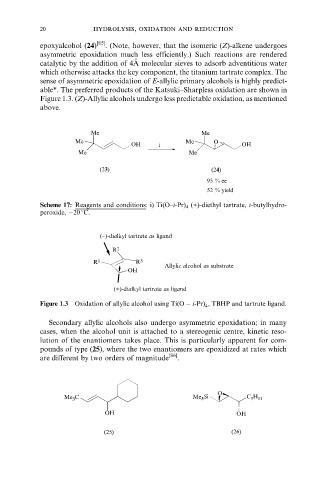
able*. The preferred products of the Katsuki±Sharpless oxidation are shown in
Figure 1.3. (Z)-Allylic alcohols undergo less predictable oxidation, as mentioned
above.
Me Me
Me Me O
OH i OH
Me Me
(23) (24)
95 % ee
52 % yield
Scheme 17: Reagents and conditions: i) Ti(O±i-Pr) 4 (+)-diethyl tartrate, t-butylhydro-
peroxide, ÿ20 8C.
(−)-dialkyl tartrate as ligand
R 2
R 1 R 3
Allylic alcohol as substrate
OH
(+)-dialkyl tartrate as ligand
Figure 1.3 Oxidation of allylic alcohol using Ti(O ÿ i-Pr) , TBHP and tartrate ligand.
4
Secondary allylic alcohols also undergo asymmetric epoxidation; in many
cases, when the alcohol unit is attached to a stereogenic centre, kinetic reso-
lution of the enantiomers takes place. This is particularly apparent for com-
pounds of type (25), where the two enantiomers are epoxidized at rates which
are different by two orders of magnitude [86] .
O
Me 3 C Me 3 Si C 5 H 11
OH OH
(25) (26)