Page 44 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 44
the integration of biotransformations into catalyst 27
of high optical purity [113] . The method is much less successful for the vast
majority of ketones.
(S)-Cyanohydrins are formed from a wide range of alkyl and aryl aldehydes
(and also some methyl ketones) often in good yield and high enantiomeric
excess using the enzyme (hydroxynitrile lyase) from Hevea brasiliensis [114] .
The same range of substrates and the same cyanohydrins ((S)-configuration)
are formed on catalysis of the addition of HCN using the hydroxynitrile lyase
from Manihot esculenta. This enzyme has been cloned and over-expressed in E.
coli [115] .
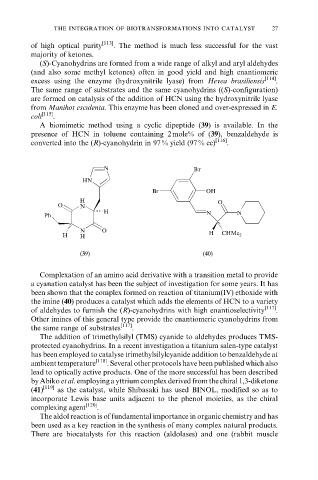
A biomimetic method using a cyclic dipeptide (39) is available. In the
presence of HCN in toluene containing 2 mole% of (39), benzaldehyde is
converted into the (R)-cyanohydrin in 97 % yield (97 % ee) [116] .
N Br
HN
Br OH
H O
O N
H N N
Ph
N O
H H H CHMe 2
(39) (40)
Complexation of an amino acid derivative with a transition metal to provide
a cyanation catalyst has been the subject of investigation for some years. It has
been shown that the complex formed on reaction of titanium(IV) ethoxide with
the imine (40) produces a catalyst which adds the elements of HCN to a variety
of aldehydes to furnish the (R)-cyanohydrins with high enantioselectivity [117] .
Other imines of this general type provide the enantiomeric cyanohydrins from
the same range of substrates [117] .
The addition of trimethylsilyl (TMS) cyanide to aldehydes produces TMS-
protected cyanohydrins. In a recent investigation a titanium salen-type catalyst
has been employed to catalyse trimethylsilylcyanide addition to benzaldehyde at
ambient temperature [118] . Several other protocols have been published which also
lead to optically active products. One of the more successful has been described
by Abiko et al. employing a yttrium complex derived from the chiral 1,3-diketone
(41) [119] as the catalyst, while Shibasaki has used BINOL, modified so as to
incorporate Lewis base units adjacent to the phenol moieties, as the chiral
complexing agent [120] .
The aldol reaction is of fundamental importance in organic chemistry and has
been used as a key reaction in the synthesis of many complex natural products.
There are biocatalysts for this reaction (aldolases) and one (rabbit muscle