Page 185 - Complete Wireless Design
P. 185
Amplifier Design
184 Chapter Three
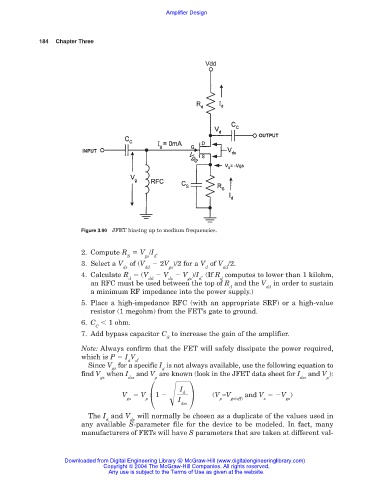
Figure 3.90 JFET biasing up to medium frequencies.
2. Compute R V /I .
S gs d
3. Select a V of (V 2V )/2 for a V of V /2.
ds dd gs d dd
4. Calculate R (V V V )/I . (If R computes to lower than 1 kilohm,
d dd ds gs d d
an RFC must be used between the top of R and the V in order to sustain
d dd
a minimum RF impedance into the power supply.)
5. Place a high-impedance RFC (with an appropriate SRF) or a high-value
resistor (1 megohm) from the FET’s gate to ground.
6. C 1 ohm.
C
7. Add bypass capacitor C to increase the gain of the amplifier.
S
Note: Always confirm that the FET will safely dissipate the power required,
which is P I V .
d d
Since V for a specific I is not always available, use the following equation to
gs d
find V when I and V are known (look in the JFET data sheet for I and V ):
gs dss p dss p
I
d
V V 1 (V ≈V and V V )
gs p I p gs(off) s gs
dss
The I and V will normally be chosen as a duplicate of the values used in
d ds
any available S-parameter file for the device to be modeled. In fact, many
manufacturers of FETs will have S parameters that are taken at different val-
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.