Page 276 - Computational Fluid Dynamics for Engineers
P. 276
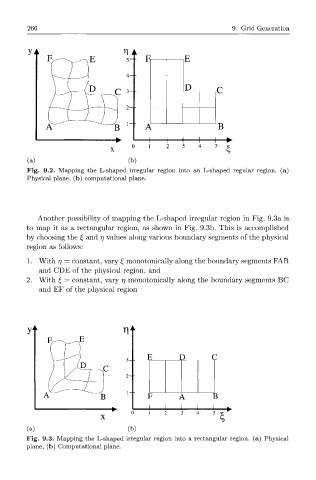
266 9. Grid Generation
b E
D
B
(a) (b)
Fig. 9.2. Mapping the L-shaped irregular region into an L-shaped regular region, (a)
Physical plane, (b) computational plane.
Another possibility of mapping the L-shaped irregular region in Fig. 9.3a is
to map it as a rectangular region, as shown in Fig. 9.3b. This is accomplished
by choosing the £ and rj values along various boundary segments of the physical
region as follows:
1. With r\ — constant, vary £ monotonically along the boundary segments FAB
and CDE of the physical region, and
2. With £ = constant, vary r\ monotonically along the boundary segments BC
and EF of the physical region
T\
E
E D C
D
— - A C
2-\-
A I |H 1 \ [ B
— •
(a) (b)
Fig. 9.3. Mapping the L-shaped irregular region into a rectangular region, (a) Physical
plane, (b) Computational plane.