Page 156 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 156
Chapter 5: Exploratory Data Analysis 143
4
2
0.1
0 0.05
−2 0
2
−4 0 0 2
−4 −2 0 2 4 −2 −2
G
U
GU
5.2
5.2
F FI F F II IG URE GU 5.2 RE RE RE 5.2 2 2 2 2
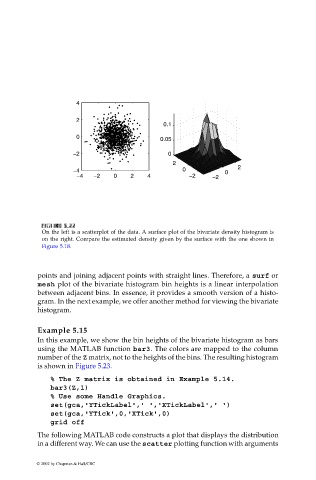
On the left is a scatterplot of the data. A surface plot of the bivariate density histogram is
on the right. Compare the estimated density given by the surface with the one shown in
Figure 5.18.
points and joining adjacent points with straight lines. Therefore, a surf or
mesh plot of the bivariate histogram bin heights is a linear interpolation
between adjacent bins. In essence, it provides a smooth version of a histo-
gram. In the next example, we offer another method for viewing the bivariate
histogram.
Example 5.15
In this example, we show the bin heights of the bivariate histogram as bars
using the MATLAB function bar3. The colors are mapped to the column
number of the Z matrix, not to the heights of the bins. The resulting histogram
is shown in Figure 5.23.
% The Z matrix is obtained in Example 5.14.
bar3(Z,1)
% Use some Handle Graphics.
set(gca,'YTickLabel',' ','XTickLabel',' ')
set(gca,'YTick',0,'XTick',0)
grid off
The following MATLAB code constructs a plot that displays the distribution
in a different way. We can use the scatter plotting function with arguments
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC