Page 269 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 269
254 Chapter 6 DSP Algorithms
the sample rate. However, the minimum iteration period can be achieved by inter-
leaving and/or pipelining.
Interleaving and pipelining are commonly used techniques to modify a partly
sequential algorithm so that the data throughput of the new algorithm becomes
higher. Both techniques can be simultaneously applied at different levels within a
system—for example, at the algorithm level and at the hardware level.
6.8.1 Interleaving
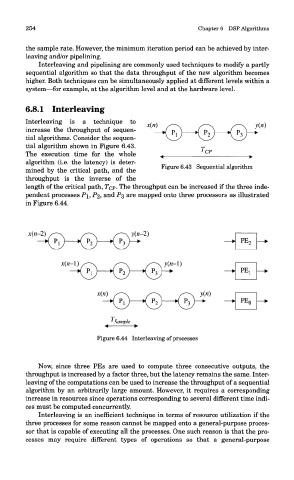
Interleaving is a technique to
increase the throughput of sequen-
tial algorithms. Consider the sequen-
tial algorithm shown in Figure 6.43.
The execution time for the whole
algorithm (i.e. the latency) is deter-
mined by the critical path, and the
throughput is the inverse of the
length of the critical path, TCP- The throughput can be increased if the three inde-
pendent processes PI, P^, and P$ are mapped onto three processors as illustrated
in Figure 6.44.
Figure 6.44 Interleaving of processes
Now, since three PEs are used to compute three consecutive outputs, the
throughput is increased by a factor three, but the latency remains the same. Inter-
leaving of the computations can be used to increase the throughput of a sequential
algorithm by an arbitrarily large amount. However, it requires a corresponding
increase in resources since operations corresponding to several different time indi-
ces must be computed concurrently.
Interleaving is an inefficient technique in terms of resource utilization if the
three processes for some reason cannot be mapped onto a general-purpose proces-
sor that is capable of executing all the processes. One such reason is that the pro-
cesses may require different types of operations so that a general-purpose