Page 372 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 372
o
O
DSP ARCHITECTURES
8.1 INTRODUCTION
Many digital signal processing applications, particularly video applications, repre-
sent very high computational work loads. Fortunately, most DSP algorithms
exhibit a high degree of parallelism and are therefore suitable for implementation
using parallel and/or distributed architectures. Such parallel architectures may
exploit future improvements in integrated circuit technologies—e.g., the fact that
it will be possible to put more circuitry onto a single chip. The expected increase in
speed of integrated circuits resulting from scaling down the size of the switching
devices will also contribute to increased performance. However, the expected per-
formance increase resulting from faster circuitry will be significantly smaller than
the increase due to the increase in the number of gates.
In this chapter we will discuss the properties of multiprocessor and multicom-
puter architectures suitable for DSP systems. Of particular interest are architec-
tures for hard real-time DSP systems—i.e., systems in which the correctness of
the system depends not only on the result of the computation, but also on the time
at which the results are produced. The architectures must therefore have
resources adequate to perform their functions.
8.2 DSP SYSTEM ARCHITECTURES
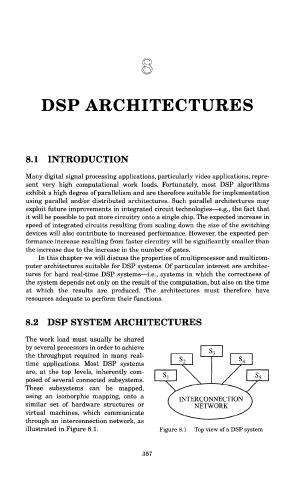
The work load must usually be shared
by several processors in order to achieve
the throughput required in many real-
time applications. Most DSP systems
are, at the top levels, inherently com-
posed of several connected subsystems.
These subsystems can be mapped,
using an isomorphic mapping, onto a
similar set of hardware structures or
virtual machines, which communicate
through an interconnection network, as
illustrated in Figure 8.1. Figure 8.1 Top view of a DSP system