Page 504 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 504
11.8 S/P Multipliers with Fixed Coefficients 489
11.8 S/P MULTIPLIERS WITH FIXED COEFFICIENTS
The multiplier can be simplified significantly if the coefficient is fixed. If a certain
bit in the coefficient is 1, then the corresponding AND gate can be replaced by a
wire. On the other hand, if a certain bit is 0, then the corresponding AND gate can
be removed. We demonstrate further possible simplifications by the means of an
example.
EXAMPLE 11.7
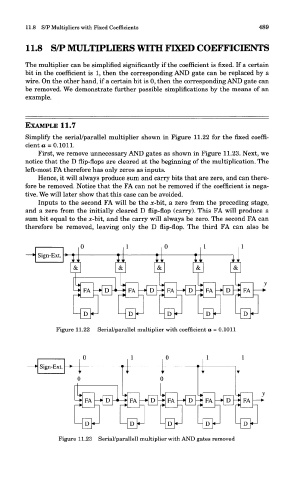
Simplify the serial/parallel multiplier shown in Figure 11.22 for the fixed coeffi-
cient a = 0.1011.
First, we remove unnecessary AND gates as shown in Figure 11.23. Next, we
notice that the D flip-flops are cleared at the beginning of the multiplication. The
left-most FA therefore has only zeros as inputs.
Hence, it will always produce sum and carry bits that are zero, and can there-
fore be removed. Notice that the FA can not be removed if the coefficient is nega-
tive. We will later show that this case can be avoided.
Inputs to the second FA will be the x-bit, a zero from the preceding stage,
and a zero from the initially cleared D flip-flop (carry). This FA will produce a
sum bit equal to the x-bit, and the carry will always be zero. The second FA can
therefore be removed, leaving only the D flip-flop. The third FA can also be
Figure 11.22 Serial/parallel multiplier with coefficient a = 0.1011
Figure 11.23 Serial/parallell multiplier with AND gates removed