Page 255 - Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
P. 255
250 Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
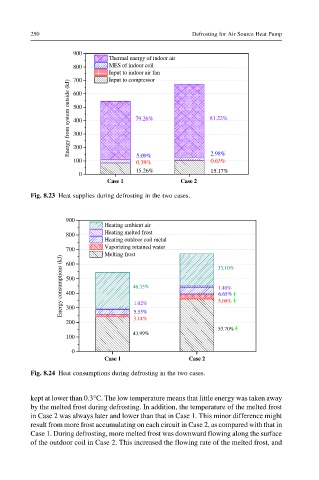
900
Thermal energy of indoor air
800 MES of indoor coil
Input to indoor air fan
Input to compressor
700
Energy from system outside (kJ) 500 79.26% 81.22%
600
400
300
200
100 5.09% 2.98%
0.63%
0.39%
15.26% 15.17%
0
Case 1 Case 2
Fig. 8.23 Heat supplies during defrosting in the two cases.
900
Heating ambient air
Heating melted frost
800
Heating outdoor coil metal
700 Vaporizing retained water
Melting frost 33.10%
Energy consumptions (kJ) 500 46.33% 1.46%
600
400
6.65%
5.09%
1.02%
300
5.53%
3.14%
200
53.70%
43.99%
100
0
C e s a 1 C e s a 2
Fig. 8.24 Heat consumptions during defrosting in the two cases.
kept at lower than 0.3°C. The low temperature means that little energy was taken away
by the melted frost during defrosting. In addition, the temperature of the melted frost
in Case 2 was always later and lower than that in Case 1. This minor difference might
result from more frost accumulating on each circuit in Case 2, as compared with that in
Case 1. During defrosting, more melted frost was downward flowing along the surface
of the outdoor coil in Case 2. This increased the flowing rate of the melted frost, and