Page 288 - Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
P. 288
282 Defrosting for Air Source Heat Pump
Fig. 9.23 Pressure difference between suction and discharge during defrosting.
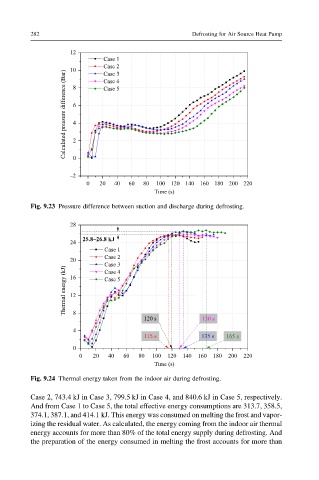
Fig. 9.24 Thermal energy taken from the indoor air during defrosting.
Case 2, 743.4 kJ in Case 3, 799.5 kJ in Case 4, and 840.6 kJ in Case 5, respectively.
And from Case 1 to Case 5, the total effective energy consumptions are 313.7, 358.5,
374.1, 387.1, and 414.1 kJ. This energy was consumed on melting the frost and vapor-
izing the residual water. As calculated, the energy coming from the indoor air thermal
energy accounts for more than 80% of the total energy supply during defrosting. And
the preparation of the energy consumed in melting the frost accounts for more than