Page 107 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 107
Chapter 4 Electrical Controls 69
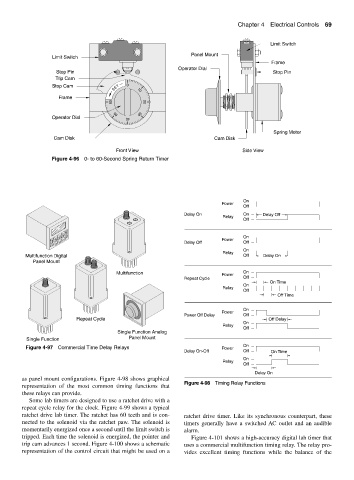
Limit Switch
Panel Mount
Limit Switch
Frame
Operator Dial
Stop Pin Stop Pin
Trip Cam
Stop Cam T 0
SE 10
Frame
60 20
50 30
Operator Dial 40
Spring Motor
Cam Disk Cam Disk
Front View Side View
Figure 4-96 0- to 60-Second Spring Return Timer
On
Power
Off
Delay On On Delay Off
Relay
Off
On
Power
Delay Off Off
On
Relay
Multifunction Digital Off Delay On
Panel Mount
Multifunction Power On
Repeat Cycle Off
On Time
On
Relay
Off
Off Time
On
Power
Power Off Delay Off
Repeat Cycle Off Delay
On
Relay
Off
Single Function Analog
Single Function Panel Mount
On
Figure 4-97 Commercial Time Delay Relays Power
Delay On-Off Off On Time
On
Relay
Off
Delay On
as panel mount configurations. Figure 4-98 shows graphical
Figure 4-98 Timing Relay Functions
representation of the most common timing functions that
these relays can provide.
Some lab timers are designed to use a ratchet drive with a
repeat cycle relay for the clock. Figure 4-99 shows a typical
ratchet drive lab timer. The ratchet has 60 teeth and is con- ratchet drive timer. Like its synchronous counterpart, these
nected to the solenoid via the ratchet paw. The solenoid is timers generally have a switched AC outlet and an audible
momentarily energized once a second until the limit switch is alarm.
tripped. Each time the solenoid is energized, the pointer and Figure 4-101 shows a high-accuracy digital lab timer that
trip cam advances 1 second. Figure 4-100 shows a schematic uses a commercial multifunction timing relay. The relay pro-
representation of the control circuit that might be used on a vides excellent timing functions while the balance of the