Page 159 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 159
Chapter 6 Rotating Components 121
Adjustment Pulley Ground Fuel Fill
Forward Housing
Core Support Frame
Output
Fuel
Tank
Engine
Power
Panel
Pivot Field Generator Recoil
Rear Housing
Starter
Figure 6-62 Typical Automobile Alternator
Rubber
Feet
Battery Clamps Figure 6-65 Single Cylinder Engine Driven Portable
Generator Set
V-Belt
Tension Bracket
Magnetos
Motor
Alternator
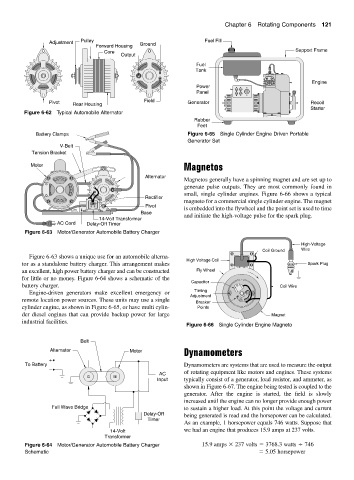
Magnetos generally have a spinning magnet and are set up to
generate pulse outputs. They are most commonly found in
small, single cylinder engines. Figure 6-66 shows a typical
Rectifier
magneto for a commercial single cylinder engine. The magnet
Pivot
is embedded into the flywheel and the point set is used to time
Base
14-Volt Transformer and initiate the high-voltage pulse for the spark plug.
AC Cord Delay-Off Timer
Figure 6-63 Motor/Generator Automobile Battery Charger
High-Voltage
Coil Ground Wire
Figure 6-63 shows a unique use for an automobile alterna-
High Voltage Coil
tor as a standalone battery charger. This arrangement makes Spark Plug
an excellent, high power battery charger and can be constructed Fly Wheel
for little or no money. Figure 6-64 shows a schematic of the
Capacitor
battery charger. Coil Wire
Engine-driven generators make excellent emergency or Timing
Adjustment
remote location power sources. These units may use a single
Breaker
cylinder engine, as shown in Figure 6-65, or have multi cylin- Points
der diesel engines that can provide backup power for large Magnet
industrial facilities.
Figure 6-66 Single Cylinder Engine Magneto
Belt
Alternator Motor Dynamometers
+
To Battery Dynamometers are systems that are used to measure the output
−
AC of rotating equipment like motors and engines. These systems
G M
Input typically consist of a generator, load resistor, and ammeter, as
shown in Figure 6-67. The engine being tested is coupled to the
generator. After the engine is started, the field is slowly
increased until the engine can no longer provide enough power
Full Wave Bridge to sustain a higher load. At this point the voltage and current
Delay-Off being generated is read and the horsepower can be calculated.
Timer
As an example, 1 horsepower equals 746 watts. Suppose that
14-Volt we had an engine that produces 15.9 amps at 237 volts.
Transformer
Figure 6-64 Motor/Generator Automobile Battery Charger 15.9 amps 237 volts 3768.3 watts 746
Schematic 5.05 horsepower