Page 155 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 155
Chapter 6 Rotating Components 117
Variable Frequency Drives
Actuator Arm
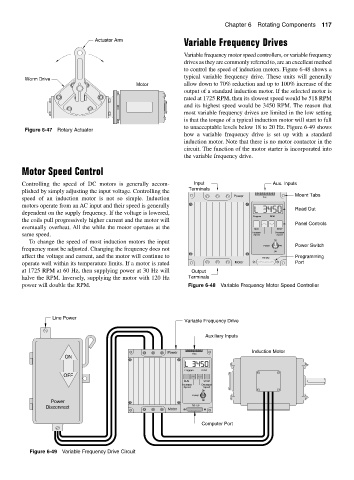
Variable frequency motor speed controllers, or variable frequency
drives as they are commonly referred to, are an excellent method
to control the speed of induction motors. Figure 6-48 shows a
typical variable frequency drive. These units will generally
Worm Drive
Motor allow down to 70% reduction and up to 100% increase of the
output of a standard induction motor. If the selected motor is
rated at 1725 RPM, then its slowest speed would be 518 RPM
and its highest speed would be 3450 RPM. The reason that
most variable frequency drives are limited in the low setting
is that the torque of a typical induction motor will start to fall
to unacceptable levels below 18 to 20 Hz. Figure 6-49 shows
Figure 6-47 Rotary Actuator
how a variable frequency drive is set up with a standard
induction motor. Note that there is no motor contactor in the
circuit. The function of the motor starter is incorporated into
the variable frequency drive.
Motor Speed Control
Controlling the speed of DC motors is generally accom- Input Aux. Inputs
plished by simply adjusting the input voltage. Controlling the Terminals Mount Tabs
speed of an induction motor is not so simple. Induction Power Aux.
motors operate from an AC input and their speed is generally
Read Out
dependent on the supply frequency. If the voltage is lowered,
Program RPM
the coils pull progressively higher current and the motor will
Panel Controls
eventually overheat. All the while the motor operates at the RUN STOP
same speed. Increase Decrease
Speed
Speed
To change the speed of most induction motors the input On
Power Power Switch
frequency must be adjusted. Changing the frequency does not
Off
affect the voltage and current, and the motor will continue to RS-232 Programming
operate well within its temperature limits. If a motor is rated Motor Port
at 1725 RPM at 60 Hz, then supplying power at 30 Hz will Output
halve the RPM. Inversely, supplying the motor with 120 Hz Terminals
power will double the RPM. Figure 6-48 Variable Frequency Motor Speed Controller
Line Power
Variable Frequency Drive
Auxiliary Inputs
Power Aux. Induction Motor
ON
Program RPM
OFF
RUN STOP
Increase Decrease
Speed Speed
On
Power
Power Off
Disconnect Motor RS-232
Computer Port
Figure 6-49 Variable Frequency Drive Circuit