Page 338 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 338
7.4 PROGRAMMABLE ARRAY LOGIC DEVICES 309
AND plane
representation
0,(L)
Programmed input
to XOR gate
(a) (b)
Output
Clock enable
0,(L)
(c)
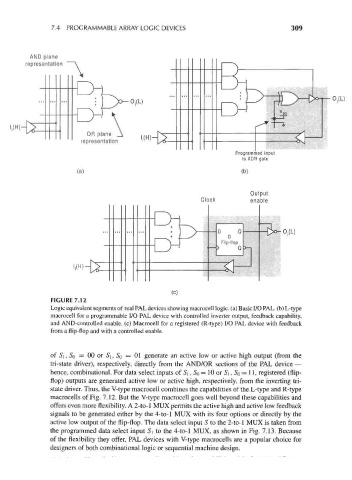
FIGURE 7.12
Logic equivalent segments of real PAL devices showing macrocell logic, (a) Basic I/O PAL. (b) L-type
macrocell for a programmable I/O PAL device with controlled inverter output, feedback capability,
and AND-controlled enable, (c) Macrocell for a registered (R-type) I/O PAL device with feedback
from a flip-flop and with a controlled enable.
of Si, So = 00 or S\, SQ = 01 generate an active low or active high output (from the
tri-state driver), respectively, directly from the AND/OR sections of the PAL device —
hence, combinational. For data select inputs of S\, SQ = 10 or Si, SQ = 11, registered (flip-
flop) outputs are generated active low or active high, respectively, from the inverting tri-
state driver. Thus, the V-type macrocell combines the capabilities of the L-type and R-type
macrocells of Fig. 7.12. But the V-type macrocell goes well beyond these capabilities and
offers even more flexibility. A 2-to-l MUX permits the active high and active low feedback
signals to be generated either by the 4-to-l MUX with its four options or directly by the
active low output of the flip-flop. The data select input S to the 2-to-l MUX is taken from
the programmed data select input S\ to the 4-to-l MUX, as shown in Fig. 7.13. Because
of the flexibility they offer, PAL devices with V-type macrocells are a popular choice for
designers of both combinational logic or sequential machine design.