Page 582 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 582
552 CHAPTER 11 / SYNCHRONOUS FSM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
(1) Run a complete output race glitch (ORG) analysis on each FSM. To do this,
follow the examples in Section 11.2. Thus, if ORGs exist, indicate their origin
and type (+ or —). Do not alter the state diagram in any way.
(2) In consideration of part (1), run a complete static hazard analysis on each of
these FSMs. To do this, follow the examples in Section 11.3. Assume that
each FSM is to be implemented with NAND-based flip-flops, and indicate
whether an existing static hazard is externally or internally initiated. Consider
both SOP and POS output-forming logic and give the gate/input tally for each,
including static hazard cover (if any). Do not alter the state code assignment
and do not construct a logic circuit for the FSM.
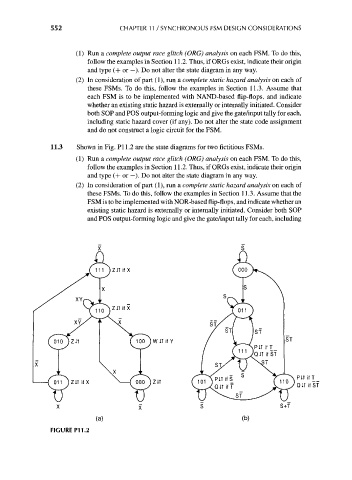
11.3 Shown in Fig. PI 1.2 are the state diagrams for two fictitious FSMs.
(1) Run a complete output race glitch (ORG) analysis on each FSM. To do this,
follow the examples in Section 11.2. Thus, if ORGs exist, indicate their origin
and type (+ or —). Do not alter the state diagram in any way.
(2) In consideration of part (1), run a complete static hazard analysis on each of
these FSMs. To do this, follow the examples in Section 11.3. Assume that the
FSM is to be implemented with NOR-based flip-flops, and indicate whether an
existing static hazard is externally or internally initiated. Consider both SOP
and POS output-forming logic and give the gate/input tally for each, including
W IT if Y
PIT if T_
Q IT if ST
S+T
(b)