Page 371 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 371
CHAPTER 10 Transmission Lines 353
and
V − 5 1 1
I − =− 1 =− − = A
1
Z 0 3 50 30
Note that no attempt is made here to derive I 1 − from I . They are both obtained
+
1
independently from their respective voltages.
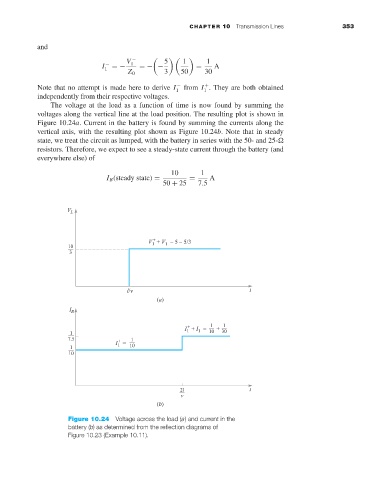
The voltage at the load as a function of time is now found by summing the
voltages along the vertical line at the load position. The resulting plot is shown in
Figure 10.24a. Current in the battery is found by summing the currents along the
vertical axis, with the resulting plot shown as Figure 10.24b. Note that in steady
state, we treat the circuit as lumped, with the battery in series with the 50- and 25-
resistors. Therefore, we expect to see a steady-state current through the battery (and
everywhere else) of
10 1
I B (steady state) = = A
50 + 25 7.5
(a)
(b)
Figure 10.24 Voltage across the load (a) and current in the
battery (b)as determined from the reflection diagrams of
Figure 10.23 (Example 10.11).