Page 307 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 307
288 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
The overall efficiency can now be written as
2
W KU 2 KU 2 U c 2 1
0 D D h D h 2K
gH E gH g c 1 2gH E
2 2
∴ 0 D R N 2K N D N . R 2K /. .9.11/
Hence, the mechanical efficiency is,
2
m D 1 2K / R . (9.12)
It can be seen that according to eqn. (9.12), as the speed ratio is reduced towards
zero, the mechanical efficiency increases and approaches unity. As there must be
some bearing friction at all speeds, however small, an additional term is needed in
2
2
the loss equation of the form Ac C kU , where A is another dimensionless constant.
0
The solution of this is left for the student to solve.
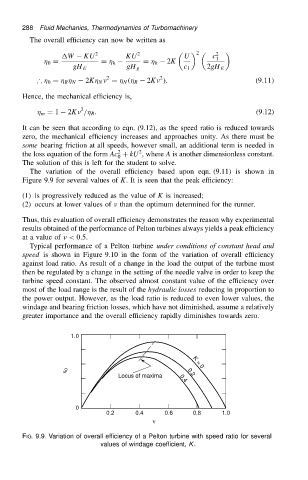
The variation of the overall efficiency based upon eqn. (9.11) is shown in
Figure 9.9 for several values of K. It is seen that the peak efficiency:
(1) is progressively reduced as the value of K is increased;
(2) occurs at lower values of than the optimum determined for the runner.
Thus, this evaluation of overall efficiency demonstrates the reason why experimental
results obtained of the performance of Pelton turbines always yields a peak efficiency
at a value of < 0.5.
Typical performance of a Pelton turbine under conditions of constant head and
speed is shown in Figure 9.10 in the form of the variation of overall efficiency
against load ratio. As result of a change in the load the output of the turbine must
then be regulated by a change in the setting of the needle valve in order to keep the
turbine speed constant. The observed almost constant value of the efficiency over
most of the load range is the result of the hydraulic losses reducing in proportion to
the power output. However, as the load ratio is reduced to even lower values, the
windage and bearing friction losses, which have not diminished, assume a relatively
greater importance and the overall efficiency rapidly diminishes towards zero.
1.0
h 0 0.2 K = 0
Locus of maxima 0.4
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
n
FIG. 9.9. Variation of overall efficiency of a Pelton turbine with speed ratio for several
values of windage coefficient, K.