Page 137 - Fluid-Structure Interactions Slender Structure and Axial Flow (Volume 1)
P. 137
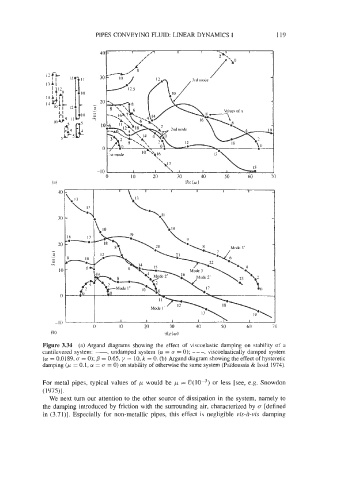
PIPES CONVEYING FLUID: LINEAR DYNAMICS I 119
(b) Qc (0)
Figure 3.34 (a) Argand diagrams showing the effect of viscoelastic damping on stability of a
cantilevered system: -, undamped system (a = o = 0); - - -, viscoelastically damped system
(a! = 0.0189, cr = 0); /? = 0.65, y = 10, k = 0. (b) Argand diagram showing the effect of hysteretic
damping (p = 0.1, a = c = 0) on stability of otherwise the same system (PaTdoussis & Issid 1974).
For metal pipes, typical values of /.L would be /.L = 6(10d3) or less [see, e.g. Snowdon
( 19731.
We next turn our attention to the other source of dissipation in the system, namely to
the damping introduced by friction with the surrounding air, characterized by 0 [defined
in (3.7 l)]. Especially for non-metallic pipes, this effect is negligible vis-&-vis damping