Page 270 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 270
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER 251
9.1.2 Condensation
. What are the different modes of condensation? Explain.
& Dropwise Condensation: In dropwise condensation,
drops of liquid are formed from vapor at particularly
favored locations, called nucleation sites, on a solid
surface. These locations can be in the form of pits or
any other surface irregularities that may be thousands
in number per unit surface area.
& The drops grow by continued condensation and
coalesce with adjacent drops, forming larger drops
that detach from the solid surface by the action of
gravity or by sweeping action by the moving vapors,
clearing the surface and exposing it to vapor.
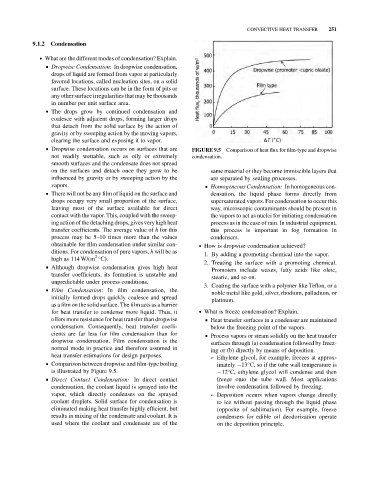
& Dropwise condensation occurs on surfaces that are Comparison of heat flux for film-type and dropwise
FIGURE 9.5
not readily wettable, such as oily or extremely condensation.
smooth surfaces and the condensate does not spread
on the surfaces and detach once they grow to be same material or they become immiscible layers that
influenced by gravity or by sweeping action by the are separated by settling processes.
vapors. & Homogeneous Condensation: In homogeneous con-
& There will not be any film of liquid on the surface and densation, the liquid phase forms directly from
drops occupy very small proportion of the surface, supersaturated vapors. For condensation to occur this
leaving most of the surface available for direct way, microscopic contaminants should be present in
contact with the vapor. This, coupled with the sweep- the vapors to act as nuclei for initiating condensation
ing action of the detaching drops, givesveryhigh heat process as in the case of rain. In industrial equipment,
transfer coefficients. The average value of h for this this process is important in fog formation in
process may be 5–10 times more than the values condensers.
obtainable for film condensation under similar con- . How is dropwise condensation achieved?
ditions. For condensation of pure vapors, h will be as
1. By adding a promoting chemical into the vapor.
high as 114 W/(m C).
2
2. Treating the surface with a promoting chemical.
& Although dropwise condensation gives high heat
Promoters include waxes, fatty acids like oleic,
transfer coefficients, its formation is unstable and
stearic, and so on.
unpredictable under process conditions.
3. Coating the surface with a polymer like Teflon, or a
& Film Condensation: In film condensation, the
noble metal like gold, silver, rhodium, palladium, or
initially formed drops quickly coalesce and spread
platinum.
as a film on the solid surface. The film acts as a barrier
for heat transfer to condense more liquid. Thus, it . What is freeze condensation? Explain.
offers more resistance for heat transfer than dropwise & Heat transfer surfaces in a condenser are maintained
condensation. Consequently, heat transfer coeffi- below the freezing point of the vapors.
cients are far less for film condensation than for & Process vapors or steam solidify on the heat transfer
dropwise condensation. Film condensation is the surfaces through (a) condensation followed by freez-
normal mode in practice and therefore assumed in ing or (b) directly by means of deposition.
heat transfer estimations for design purposes. ➢ Ethylene glycol, for example, freezes at approx-
& Comparison between dropwise and film-type boiling imately 13 C, so if the tube wall temperature is
is illustrated by Figure 9.5. 12 C, ethylene glycol will condense and then
& Direct Contact Condensation: In direct contact freeze onto the tube wall. Most applications
condensation, the coolant liquid is sprayed into the involve condensation followed by freezing.
vapor, which directly condenses on the sprayed ➢ Deposition occurs when vapors change directly
coolant droplets. Solid surface for condensation is to ice without passing through the liquid phase
eliminated making heat transfer highly efficient, but (opposite of sublimation). For example, freeze
results in mixing of the condensate and coolant. It is condensers for edible oil deodorization operate
used where the coolant and condensate are of the on the deposition principle.