Page 426 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 426
Lube, Seal and Control Oil System Best Practices Best Practice 7 .15
ported valve should be designed with a lifting jack when a taper
plug is used. This feature allows transfer of valves from one bank
to another easily and still ensures tight shutoff of the valve when
in its proper position.
Selection of valves should consider material and sizing. Ma-
terials of construction should be carbon steel as a minimum,
with stainless steel internals. Bronze components should not be
considered in systems that can incorporate gas entrained in the
system fluid; in such systems brass, copper or bronze is not
permitted. Valves are sized to match piping sizes in the system
which are normally designed for fluid velocities of four (4) to six
(6) feet per second.
Reliability considerations
As previously mentioned, transfer valves that include lifting
jacks are susceptible to valve plug damage. Frequently operators
do not employ lifting jacks when transferring valves. This type of
valve can become bound and even break the stem, thus neces-
sitating critical equipment shutdown. Prior to transferring flow
from one bank to another, the bank to be transferred to must be
full of auxiliary system fluid and properly vented. If it is not, the
capacity of coolers, filters and piping in the bank to be trans-
ferred to act as a vessel and consequently reduce flow and
pressure to the critical equipment which will cause shutdown of
the unit. Also, improperly vented components containing air or
gases can cause control valve instabilities which can also lead to
equipment shutdown.
Coolers
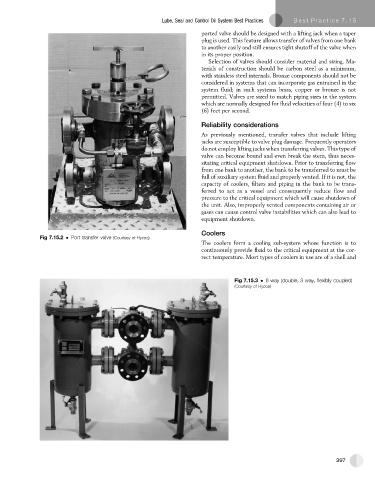
Fig 7.15.2 Port transfer valve (Courtesy of Hycoa)
The coolers form a cooling sub-system whose function is to
continuously provide fluid to the critical equipment at the cor-
rect temperature. Most types of coolers in use are of a shell and
Fig 7.15.3 6 way (double, 3 way, flexibly coupled)
(Courtesy of Hycoa)
397