Page 244 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 244
224 PASSIVE SEISMIC METHODS FOR UNCONVENTIONAL RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
REC_CNTR (receiver index counter)
1 59 114 164 224 274 332 384
18400 18400
18600 18600
18800 18800
3 19000 19000
2 19200 19200
Time (milliseconds) 19600 19600 Time (milliseconds)
19400
19400
1 19800 19800
20000
20200
20200 20000
20400 20400
20600 20600
20800 20800
21000 21000
REC_CNTR (receiver index counter)
1134 658 62 667 430
18400 18400
1 2 3 18600 18600
18800 18800
19000 19000
19200 19200
Time (milliseconds) 19600 19600 Time (milliseconds)
19400
19400
19800
19800
20000
20200 20000
20200
20400 20400
20600 20600
20800 20800
21000 21000
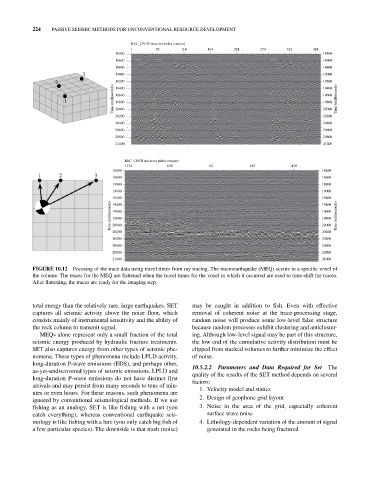
FIGURE 10.12 Focusing of the trace data using travel times from ray tracing. The microearthquake (MEQ) occurs in a specific voxel of
the volume. The traces for the MEQ are flattened when the travel times for the voxel in which it occurred are used to time‐shift the traces.
After flattening, the traces are ready for the imaging step.
total energy than the relatively rare, large earthquakes. SET may be caught in addition to fish. Even with effective
captures all seismic activity above the noise floor, which removal of coherent noise at the trace‐processing stage,
consists mainly of instrumental sensitivity and the ability of random noise will produce some low‐level false structure
the rock column to transmit signal. because random processes exhibit clustering and anticluster
MEQs alone represent only a small fraction of the total ing. Although low‐level signal may be part of this structure,
seismic energy produced by hydraulic fracture treatments. the low end of the cumulative activity distribution must be
SET also captures energy from other types of seismic phe clipped from stacked volumes to further minimize the effect
nomena. These types of phenomena include LPLD activity, of noise.
long‐duration P‐wave emissions (EDS), and perhaps other, 10.5.2.2 Parameters and Data Required for Set The
as‐yet‐undiscovered types of seismic emissions. LPLD and quality of the results of the SET method depends on several
long‐duration P‐wave emissions do not have distinct first factors:
arrivals and may persist from many seconds to tens of min 1. Velocity model and statics
utes or even hours. For these reasons, such phenomena are
ignored by conventional seismological methods. If we use 2. Design of geophone grid layout
fishing as an analogy, SET is like fishing with a net (you 3. Noise in the area of the grid, especially coherent
catch everything), whereas conventional earthquake seis surface wave noise
mology is like fishing with a lure (you only catch big fish of 4. Lithology‐dependent variation of the amount of signal
a few particular species). The downside is that trash (noise) generated in the rocks being fractured