Page 248 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 248
228 PASSIVE SEISMIC METHODS FOR UNCONVENTIONAL RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
34,500
35,000
35,500
Time (ms) 36,000
36,500
37,000
37,500
34,500
35,000
35,500
Time (ms) 36,000
36,500
37,000
37,500
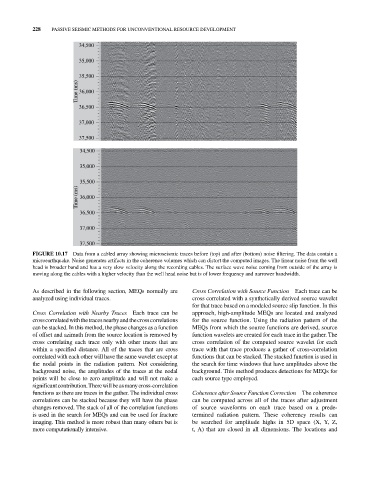
FIGURE 10.17 Data from a cabled array showing microseismic traces before (top) and after (bottom) noise filtering. The data contain a
microearthquake. Noise generates artifacts in the coherence volumes which can distort the computed images. The linear noise from the well
head is broader band and has a very slow velocity along the recording cables. The surface wave noise coming from outside of the array is
moving along the cables with a higher velocity than the well head noise but is of lower frequency and narrower bandwidth.
As described in the following section, MEQs normally are Cross Correlation with Source Function Each trace can be
analyzed using individual traces. cross correlated with a synthetically derived source wavelet
for that trace based on a modeled source slip function. In this
Cross Correlation with Nearby Traces Each trace can be approach, high‐amplitude MEQs are located and analyzed
cross correlated with the traces nearby and the cross correlations for the source function. Using the radiation pattern of the
can be stacked. In this method, the phase changes as a function MEQs from which the source functions are derived, source
of offset and azimuth from the source location is removed by function wavelets are created for each trace in the gather. The
cross correlating each trace only with other traces that are cross correlation of the computed source wavelet for each
within a specified distance. All of the traces that are cross trace with that trace produces a gather of cross‐correlation
correlated with each other will have the same wavelet except at functions that can be stacked. The stacked function is used in
the nodal points in the radiation pattern. Not considering the search for time windows that have amplitudes above the
background noise, the amplitudes of the traces at the nodal background. This method produces detections for MEQs for
points will be close to zero amplitude and will not make a each source type employed.
significant contribution. There will be as many cross‐correlation
functions as there are traces in the gather. The individual cross Coherence after Source Function Correction The coherence
correlations can be stacked because they will have the phase can be computed across all of the traces after adjustment
changes removed. The stack of all of the correlation functions of source waveforms on each trace based on a prede
is used in the search for MEQs and can be used for fracture termined radiation pattern. These coherency results can
imaging. This method is more robust than many others but is be searched for amplitude highs in 5D space (X, Y, Z,
more computationally intensive. t, A) that are closed in all dimensions. The locations and