Page 532 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 532
Adsorption 487
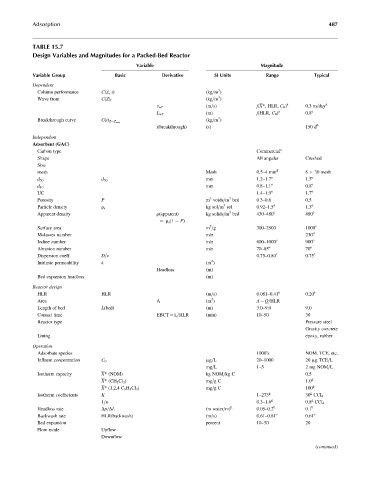
TABLE 15.7
Design Variables and Magnitudes for a Packed-Bed Reactor
Variable Magnitude
Variable Group Basic Derivative SI Units Range Typical
Dependent
3
Column performance C(Z, t) (kg=m )
3
Wave front C(Z) t (kg=m )
v wf (m=s) f(X*, HLR, C 0 ) a 0.3 m=day a
a a
(m) f(HLR, C 0 ) 0.8
L wf
3
Breakthrough curve C(t) Z¼Z max (kg=m )
b
t(breakthrough) (s) 150 d
Independent
Adsorbent (GAC)
Carbon type Commercial c
Shape All angular Crushed
Size
mesh Mesh 0.5–4mm d 8 30 mesh
d 50 d 50 mm 1.2–1.7 e 1.5 e
mm 0.8–1.1 e 0.8 e
d 10
UC 1.4–1.9 e 1.7 e
3 3
Porosity P m voids=m bed 0.3–0.6 0.5
3
Particle density r s kg sol=m sol 0.92–1.5 e 1.3 e
3
Apparent density r(apparent) kg solids=m bed 430–480 e 480 e
¼ r s (1 P)
2
Surface area m =g 300–2500 1000 e
Molasses number min 230 d
Iodine number min 600–1000 e 900 e
Abrasion number min 70–85 e 70 e
Dispersion coeff. D=v 0.75–0.80 f 0.75 f
2
Intrinsic permeability k (m )
Headloss (m)
Bed expansion headloss (m)
Reactor design
HLR HLR (m=s) 0.081–0.41 e 0.20 e
2
Area A (m ) A ¼ Q=HLR
Length of bed L(bed) (m) 3.0–9.0 9.0
Contact time EBCT ¼ L=HLR (min) 10–50 30
Reactor type Pressure steel
Gravity concrete
Lining epoxy, rubber
Operation
Adsorbate species 1000’s NOM, TCE, etc.
Influent concentration C 0 mg=L 20–1000 20 mg TCE=L
mg=L 1–5 2 mg NOM=L
Isotherm capacity X* (NOM) kg NOM=kg C 0.5
X* (CH 2 Cl 2 ) mg=g C 1.0 g
X* (1,2,4 C 6 H 3 Cl 3 ) mg=g C 100 g
g
Isotherm coefficients K 1–273 g 30 CCl 4
g
1=n 0.3–1.6 g 0.8 CCl 4
Headloss rate Dp=DL (m water=m) h 0.05–0.2 h 0.1 h
Backwash rate HLR(backwash) (m=s) 0.61–0.81 e 0.61 e
Bed expansion percent 10–50 20
Flow mode Upflow
Downflow
(continued)