Page 129 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 129
Alkanolamines for Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide Reinoval 11 9
040rrrrT-r
3
VAPOR LEAVING STRIPPING
SECTION OF COWMN
QM
a
P
3 SOLUTION 17Ya MEA.PRESSURE
s 24 PSlG AT REBOILER
B
g a20
4
E
2 -
P
*-
0.10
lTlON
PLATE
0- 1 1 I I 1
o a 4 0.00s a012 0.016 a020 a024 01
X. HOLE FRACTION CQ IN LlOUlO
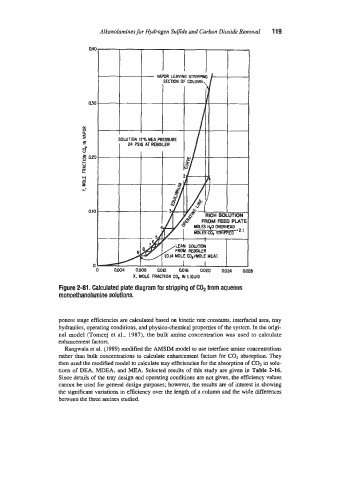
Figure 2-81. Calculated plate diagram for stripping of C02 from aqueous
monoethanolamine solutions.
ponent stage efficiencies rn calculated based on kinetic rate constants, interfacial area, tray
hydraulics, operating conditions, and physico-chemical properties of the system. In the origi-
nal model [Tomcej et al.. 1987), the bulk amine concentration was used to calculate
enhancement factors.
Rangwala et al. (1989) modified the AMSIM model to use interface amine concentrations
rather than bulk concentrations to calculate enhancement factors for C02 absorption. They
then used the modified model to calculate tray efficiencies for the absorption of COz in solu-
tions of DEA, MDEA, and MEA. Selected results of this study are given in Table 2-16.
Since details of the tray design and operating conditions are not given, the efficiency values
cannot be used for general design purposes; however, the results are of interest in showing
the significant variations in efficiency over the length of a column and the wide differences
between the three amines s~died.