Page 784 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 784
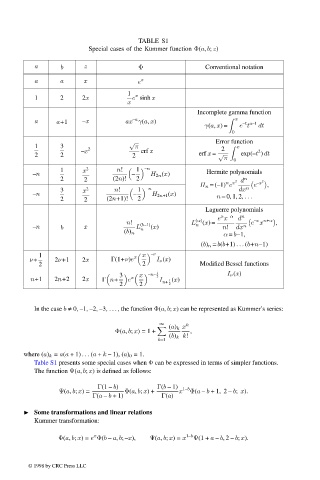
TABLE S1
Special cases of the Kummer function Φ(a, b; z)
a b z Φ Conventional notation
a a x e x
1 x
1 2 2x e sinh x
x
Incomplete gamma function
–a
a a+1 –x ax γ(a, x) x –t a–1
γ(a, x)= e t dt
0
√ Error function
1 3 2 π x
–x erf x 2 2
2 2 2 erf x = √ π 0 exp(–t ) dt
1 x 2 n! 1 –n Hermite polynomials
–n – H 2n (x)
2 2 (2n)! 2 2 d n 2
n x
H n =(–1) e e –x ,
3 x 2 n! 1 –n dx n
–n – H 2n+1 (x) n =0,1,2, ...
2 2 (2n+1)! 2
Laguerre polynomials
x –α
e x d n
–x n+α
n! (b–1) L (α) (x)= e x ,
n
–n b x L n (x) n! dx n
(b) n
α = b–1,
(b) n = b(b+1) ... (b+n–1)
x
1 x –ν
ν+ 2ν+1 2x Γ(1+ν)e I ν (x)
2 2 Modified Bessel functions
3 x 2
–n– 1 I ν (x)
n+1 2n+2 2x Γ n+ e x I n+ 1 (x)
2 2 2
In the case b ≠ 0, –1, –2, –3, ... , the function Φ(a, b; x) can be represented as Kummer’s series:
∞ k
(a) k x
Φ(a, b; x)=1 + ,
(b) k k!
k=1
where (a) k = a(a +1) ... (a + k – 1), (a) 0 =1.
Table S1 presents some special cases when Φ can be expressed in terms of simpler functions.
The function Ψ(a, b; x)isdefined as follows:
Γ(1 – b) Γ(b – 1) 1–b
Ψ(a, b; x)= Φ(a, b; x)+ x Φ(a – b +1, 2 – b; x).
Γ(a – b +1) Γ(a)
Some transformations and linear relations
Kummer transformation:
x
Φ(a, b; x)= e Φ(b – a, b; –x), Ψ(a, b; x)= x 1–b Ψ(1 + a – b,2 – b; x).
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 769