Page 166 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 166
4.2 Electrochemical Properties of EMD 135
(milliamperes hour) if the mixing and packing technique is practiced thoroughly
and the same graphite is used. However, the measured voltage has a considerable
effect on the IR drop [15]. In 1992, Kozawa et al. [16] proposed an easy, repeatable
test method using Teflonized acetylene black (TAB) developed by the Bulgarian
laboratory [17]. The three useful TABs available today are shown in Table 4.5.
TABS are a mixture of a Teflon emulsion and acetylene black, which is prepared
by a special vigorous mixing technique.
They are very useful not only for testing. They are being used in practical
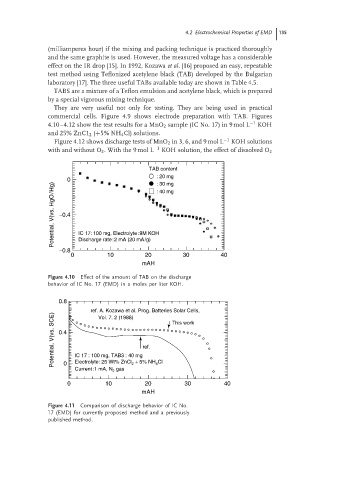
commercial cells. Figure 4.9 shows electrode preparation with TAB. Figures
4.10–4.12 show the test results for a MnO 2 sample (IC No. 17) in 9 mol L −1 KOH
and 25% ZnC1 2 (+5% NH 4 Cl) solutions.
Figure 4.12 shows discharge tests of MnO 2 in 3, 6, and 9 mol L −1 KOH solutions
with and without O 2 .Withthe 9 mol L −1 KOH solution, the effect of dissolved O 2
TAB content
: 20 mg
0 : 30 mg
Potential, V(vs. HgO/Hg) −0.4
: 40 mg
Discharge rate:2 mA (20 mA/g)
−0.8 IC 17:100 mg, Electrolyte:9M KOH
0 10 20 30 40
mAH
Figure 4.10 Effect of the amount of TAB on the discharge
behavior of IC No. 17 (EMD) in a moles per liter KOH.
0.8
ref. A. Kozawa et al. Prog. Batteries Solar Cells,
Potential, V(vs. SCE) 0.4 ref.
Vol. 7. 2 (1988)
This work
IC 17 : 100 mg, TAB3 : 40 mg
Electrolyte: 25 Wt% ZnCl + 5% NH Cl
0
Current:1 mA, N gas 2 4
2
0 10 20 30 40
mAH
Figure 4.11 Comparison of discharge behavior of IC No.
17 (EMD) for currently proposed method and a previously
published method.