Page 163 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 163
132 4 Electrochemistry of Manganese Oxides
MnO 2
(Solid Oxide) H +
+
[H ]
Solution X
in pore
+
H Concentration
gradient + −
H H O OH
2
+
η (H solid)
c
η (∆pH)
η a c
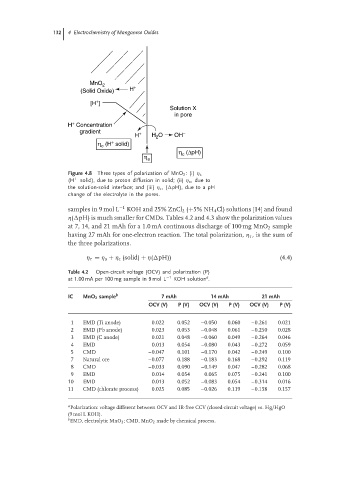
Figure 4.8 Three types of polarization of MnO 2 :(i) η c
(H + solid), due to proton diffusion in solid; (ii) η a ,due to
the solution-solid interface; and (iii) η c ,( pH), due to a pH
change of the electrolyte in the pores.
samples in 9 mol L −1 KOH and 25% ZnCl 2 (+5% NH 4 Cl) solutions [14] and found
η( pH) is much smaller for CMDs. Tables 4.2 and 4.3 show the polarization values
at 7, 14, and 21 mAh for a 1.0 mA continuous discharge of 100 mg MnO 2 sample
having 27 mAh for one-electron reaction. The total polarization, η τ ,isthe sum of
the three polarizations.
η τ = η a + η c (solid) + η( pH)) (4.4)
Table 4.2 Open-circuit voltage (OCV) and polarization (P)
a
at 1.00 mA per 100 mg sample in 9 mol L −1 KOH solution .
IC MnO 2 sample b 7mAh 14mAh 21mAh
OCV (V) P (V) OCV (V) P (V) OCV (V) P (V)
1 EMD (Ti anode) 0.022 0.052 –0.050 0.060 –0.261 0.021
2 EMD (Pb anode) 0.023 0.053 –0.048 0.061 –0.250 0.028
3 EMD (C anode) 0.021 0.048 –0.060 0.049 –0.264 0.046
4 EMD 0.013 0.054 –0.080 0.043 –0.272 0.059
5 CMD –0.047 0.101 –0.170 0.042 –0.249 0.100
7 Natural ore –0.077 0.188 –0.183 0.168 –0.292 0.119
8 CMD –0.033 0.090 –0.149 0.047 –0.282 0.068
9 EMD 0.014 0.054 0.065 0.075 –0.241 0.100
10 EMD 0.013 0.052 –0.083 0.054 –0.314 0.016
11 CMD (chlorate process) 0.025 0.085 –0.026 0.119 –0.158 0.157
a
Polarization: voltage different between OCV and IR-free CCV (closed-circuit voltage) vs. Hg/HgO
(9 mol L KOH).
b
EMD, electrolytic MnO 2 ;CMD, MnO 2 made by chemical process.