Page 164 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 164
4.2 Electrochemical Properties of EMD 133
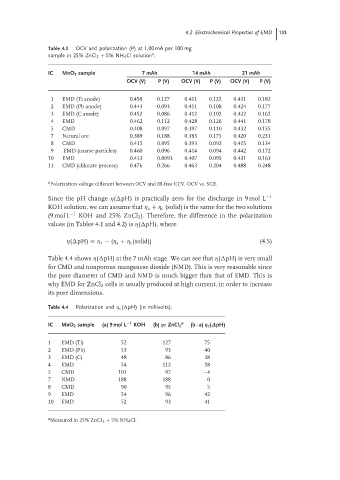
Table 4.3 OCV and polarization (P) at 1.00 mA per 100 mg
sample in 25% ZnCl 2 + 5% NH 4 Cl solution . a
IC MnO 2 sample 7 mAh 14 mAh 21 mAh
OCV (V) P (V) OCV (V) P (V) OCV (V) P (V)
1 EMD (Ti anode) 0.458 0.127 0.411 0.122 0.431 0.182
2 EMD (Pb anode) 0.443 0.093 0.411 0.108 0.424 0.177
3 EMD (C anode) 0.452 0.086 0.412 0.102 0.422 0.162
4 EMD 0.462 0.112 0.428 0.126 0.441 0.178
5 CMD 0.408 0.097 0.397 0.110 0.432 0.155
7 Natural ore 0.389 0.188 0.383 0.175 0.420 0.231
8 CMD 0.415 0.095 0.393 0.092 0.415 0.134
9 EMD (coarse particles) 0.460 0.096 0.414 0.094 0.442 0.172
10 EMD 0.453 0.0093 0.407 0.095 0.431 0.163
11 CMD (chlorate process) 0.476 0.266 0.463 0.204 0.488 0.248
a Polarization voltage different between OCV and IR-free CCV. OCV vs. SCE.
Since the pH change η( pH) is practically zero for the discharge in 9 mol L −1
KOH solution, we can assume that η a + η c (solid) is the same for the two solutions
(9 mol L −1 KOH and 25% ZnCl 2 ). Therefore, the difference in the polarization
values (in Tables 4.1 and 4.2) is η( pH), where
η( pH) = η τ − (η a + η c (solid)) (4.5)
Table 4.4 shows η( pH) at the 7 mAh stage. We can see that η( pH) is very small
for CMD and nonporous manganese dioxide (NMD). This is very reasonable since
the pore diameter of CMD and NMD is much bigger than that of EMD. This is
why EMD for ZnCl 2 cells is usually produced at high current, in order to increase
its pore dimensions.
Table 4.4 Polarization and η c ( pH) (in millivolts).
IC MnO 2 sample (a) 9 mol L −1 KOH (b) η T ZnCl 2 a (b–a) η c (∆pH)
1 EMD (Ti) 52 127 75
2 EMD (Pb) 53 93 40
3 EMD (C) 48 86 38
4 EMD 54 112 58
5 CMD 101 97 –4
7 NMD 188 188 0
8 CMD 90 95 5
9 EMD 54 96 42
10 EMD 52 93 41
a
Measured in 25% ZnCI 2 + 5% NH 4 Cl.