Page 169 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 169
138 4 Electrochemistry of Manganese Oxides
Table 4.7 Specification and typical analysis.
Component Specification Typical analysis
MnO 2 91.0% min. 92.0%
Mn 60.0% min. 60.4%
H 2 O 2.0% min. 1.8%
HCl insoluble 0.2% min. 0.02%
SO 4 1.3% min. 1.20%
Fe 150 ppm max. 80 ppm
Pb 5 ppm max. <1 ppm
Cu 5 ppm max. 1 ppm
Ni 10 ppm max. 3 ppm
Co 15 ppm max. 3 ppm
Sb 15 ppm max. <1 ppm
As 1 ppm max. <1 ppm
Mo 5 ppm max. 1 ppm
Cr 15 ppm max. 5 ppm
V 2 ppm max. <1 ppm
K 0.15% max. 0.08%
PH
JIS method a 5.0–5.6 5.2
USA method 8.0–9.0 8.5
a Neutralization with NH 4 OH or NaOH. JEC Sample, 1997. available from
ITE Japanese Office.
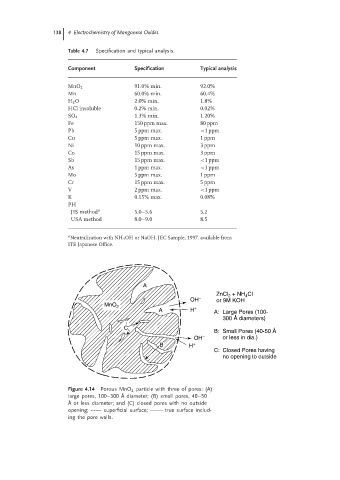
A
ZnCl + NH Cl
4
2
OH − or 9M KOH
MnO 2 +
A H A: Large Pores (100-
300 Å diameters)
C
B: Small Pores (40-50 Å
OH − or less in dia.)
B H +
C: Closed Pores having
no opening to outside
Figure 4.14 Porous MnO 2 particle with three of pores: (A)
large pores, 100–300 ˚ A diameter; (B) small pores, 40–50
˚ A or less diameter; and (C) closed pores with no outside
opening; ------- superficial surface; true surface includ-
ing the pore walls.