Page 420 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 420
418 CHAPTER 16 Degradation of protective PVD coatings
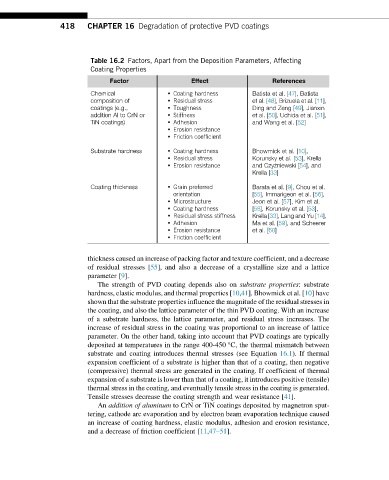
Table 16.2 Factors, Apart from the Deposition Parameters, Affecting
Coating Properties
Factor Effect References
Chemical • Coating hardness Batista et al. [47], Batista
composition of • Residual stress et al. [48], Brizuela et al. [11],
coatings (e.g., • Toughness Ding and Zeng [49], Jianxin
addition Al to CrN or • Stiffness et al. [50], Uchida et al. [51],
TiN coatings) • Adhesion and Wang et al. [52]
• Erosion resistance
• Friction coefficient
Substrate hardness • Coating hardness Bhowmick et al. [10],
• Residual stress Korunsky et al. [53], Krella
• Erosion resistance and Czyz ˙niewski [54], and
Krella [33]
Coating thickness • Grain preferred Barata et al. [9], Chou et al.
orientation [55], Immarigeon et al. [56],
• Microstructure Jeon et al. [57], Kim et al.
• Coating hardness [58], Korunsky et al. [53],
• Residual stress stiffness Krella [33], Lang and Yu [14],
• Adhesion Ma et al. [59], and Scheerer
• Erosion resistance et al. [60]
• Friction coefficient
thickness caused an increase of packing factor and texture coefficient, and a decrease
of residual stresses [55], and also a decrease of a crystalline size and a lattice
parameter [9].
The strength of PVD coating depends also on substrate properties: substrate
hardness, elastic modulus, and thermal properties [10,41]. Bhowmick et al. [10] have
shown that the substrate properties influence the magnitude of the residual stresses in
the coating, and also the lattice parameter of the thin PVD coating. With an increase
of a substrate hardness, the lattice parameter, and residual stress increases. The
increase of residual stress in the coating was proportional to an increase of lattice
parameter. On the other hand, taking into account that PVD coatings are typically
deposited at temperatures in the range 400-450 °C, the thermal mismatch between
substrate and coating introduces thermal stresses (see Equation 16.1). If thermal
expansion coefficient of a substrate is higher than that of a coating, then negative
(compressive) thermal stress are generated in the coating. If coefficient of thermal
expansion of a substrate is lower than that of a coating, it introduces positive (tensile)
thermal stress in the coating, and eventually tensile stress in the coating is generated.
Tensile stresses decrease the coating strength and wear resistance [41].
An addition of aluminum to CrN or TiN coatings deposited by magnetron sput-
tering, cathode arc evaporation and by electron beam evaporation technique caused
an increase of coating hardness, elastic modulus, adhesion and erosion resistance,
and a decrease of friction coefficient [11,47–51].