Page 186 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 186
HYDC05 12/5/05 5:35 PM Page 169
Groundwater investigation techniques 169
channel. Interflow is water moving laterally within
the soil zone in the direction of the topographic slope
and is potentially accelerated by flow through field
drains. Together, overland flow and interflow repres-
ent the quickflow or surface runoff from a stream
catchment. Baseflow is the component of total runoff
contributed by groundwater discharge as springs
or seepages and supports surface flows during dry
periods when there is little or no rainfall. From the
perspective of groundwater resources investigations,
techniques of baseflow separation from the quickflow
component are useful in contributing to an assess-
ment of groundwater recharge (see Section 5.5.1).
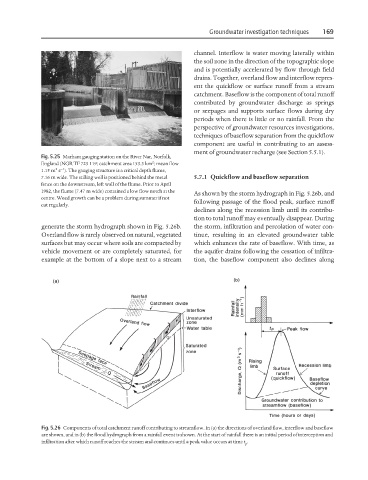
Fig. 5.25 Marham gauging station on the River Nar, Norfolk,
2
England (NGR TF 723 119; catchment area 153.3 km ; mean flow
3 −1
1.15 m s ). The gauging structure is a critical depth flume,
7.16 m wide. The stilling well is positioned behind the metal 5.7.1 Quickflow and baseflow separation
fence on the downstream, left wall of the flume. Prior to April
1982, the flume (7.47 m wide) contained a low flow notch at the
As shown by the storm hydrograph in Fig. 5.26b, and
centre. Weed growth can be a problem during summer if not
following passage of the flood peak, surface runoff
cut regularly.
declines along the recession limb until its contribu-
tion to total runoff may eventually disappear. During
generate the storm hydrograph shown in Fig. 5.26b. the storm, infiltration and percolation of water con-
Overland flow is rarely observed on natural, vegetated tinue, resulting in an elevated groundwater table
surfaces but may occur where soils are compacted by which enhances the rate of baseflow. With time, as
vehicle movement or are completely saturated, for the aquifer drains following the cessation of infiltra-
example at the bottom of a slope next to a stream tion, the baseflow component also declines along
Fig. 5.26 Components of total catchment runoff contributing to streamflow. In (a) the directions of overland flow, interflow and baseflow
are shown, and in (b) the flood hydrograph from a rainfall event is shown. At the start of rainfall there is an initial period of interception and
infiltration after which runoff reaches the stream and continues until a peak value occurs at time t .
p