Page 53 - Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
P. 53
40 Industrial Cutting of Textile Materials
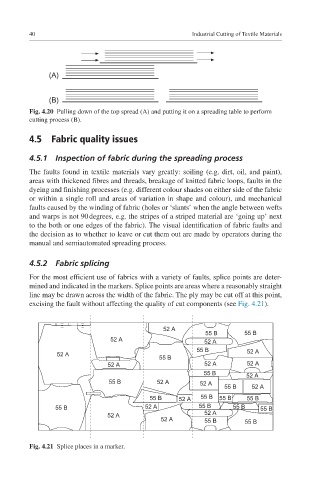
(A)
(B)
Fig. 4.20 Pulling down of the top spread (A) and putting it on a spreading table to perform
cutting process (B).
4.5 Fabric quality issues
4.5.1 Inspection of fabric during the spreading process
The faults found in textile materials vary greatly: soiling (e.g. dirt, oil, and paint),
areas with thickened fibres and threads, breakage of knitted fabric loops, faults in the
dyeing and finishing processes (e.g. different colour shades on either side of the fabric
or within a single roll and areas of variation in shape and colour), and mechanical
faults caused by the winding of fabric (holes or ‘slants’ when the angle between wefts
and warps is not 90 degrees, e.g. the stripes of a striped material are ‘going up’ next
to the both or one edges of the fabric). The visual identification of fabric faults and
the decision as to whether to leave or cut them out are made by operators during the
manual and semiautomated spreading process.
4.5.2 Fabric splicing
For the most efficient use of fabrics with a variety of faults, splice points are deter-
mined and indicated in the markers. Splice points are areas where a reasonably straight
line may be drawn across the width of the fabric. The ply may be cut off at this point,
excising the fault without affecting the quality of cut components (see Fig. 4.21).
52 A
55 B 55 B
52 A 52 A
55 B 52 A
52 A
55 B
52 A 52 A 52 A
55 B 52 A
55 B 52 A 52 A
55 B 52 A
55 B 52 A 55 B 55 B 55 B
55 B 52 A 55 B 55 B 55 B
52 A 52 A
52 A 55 B 55 B
Fig. 4.21 Splice places in a marker.