Page 463 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 463
Testing of metal-enclosed switchgear assemblies 14/437
and their vulnerability to such effects. Our present Temperature of the
discussions relate to shocks and vibrations caused by an Rigid Plates (= 20 Nos.) deepest parts of the
earthquakes and laboratory testing of equipment mounted floating on the mantle in crust can go up to
870°C
the lithosphere
on primary systems against such effects, particularly those
required for critical areas of an NPP. Molten mantle
hot rock and
Causes of seismic disturbances
Scientists suggest different theories for the causes of an
earthquake. One of many such theories is the Elastic
Rebound Theory. This suggests that with the evolution
of the earth, several tectonic processes have been taking
place within it. These processes have caused severe
deformations in the crust and have resulted in the formation
of ocean basins and mountains. These impose elastic
strains on the earth’s crust. These strains build up with
the passage of time, and eventually they overcome the
resilience of the earth’s crust and result in its rupture.
The rebound of the ruptured crust causes an earthquake.
Geologists and seismologists have explained this theory
more comprehen-sively through the Plate Tectonic Theory
which can be briefly explained as follows.
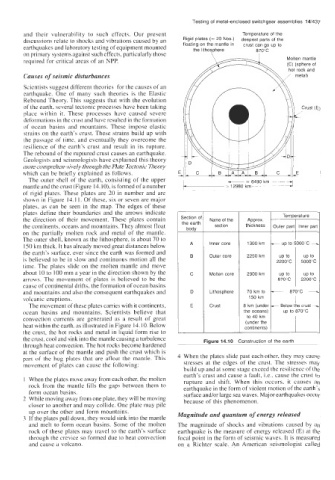
The outer shell of the earth, consisting of the upper - km -- --
6490
=
mantle and the crust (Figure 14.10), is formed ofa number =I2980 km--- --J
of rigid plates. These plates are 20 in number and are
shown in Figure 14.1 1. Of these, six or seven are major
plates, as can be seen in the map. The edges of these
plates define their boundaries and the arrows indicate Name of the 1 Temperature
the direction of their movement. These plates contain Section of Approx.
the continents, oceans and mountains. They almost float the earth section thickness Outer pari Inner part
body
on the partially molten rock and metal of the mantle.
The outer shell, known as the lithosphere, is about 70 to
150 km thick. It has already moved great distances below A Inner core
the earth’s surface, ever since the earth was formed and B Outer core
is believed to be in slow and continuous motion all the
time. The plates slide on the molten mantle and move
about IO to 100 mm a year in the direction shown by the C Molten core up to
arrows. The movement of plates is believed to be the 870°C 2200°C
cause of continental drifts, the formation of ocean basins 870°C -
and mountains and also the consequent earthquakes and D Lithosphere 70 km to
volcanic eruptions. 150 km I
The movement of these plates carries with it continents, E Crust
ocean basins and mountains. Scientists believe that
convection currents are generated as a result of great to 40 km
(under the
heat within the earth, as illustrated in Figure 14. IO. Below continents)
the crust, the hot rocks and metal in liquid form rise to
the crust, cool and sink into the mantle causing a turbulence Figure 14.10 Construction of the earth
through heat convection. The hot rocks become hardened
at the surface of the mantle and push the crust which is
part of the hug plates that are afloat the mantle. This 4 When the plates slide past each other, they may cause
movement of plates can cause the following: stresses at the edges of the crust. The stresses may
build up and at some stage exceed the rcsilicncc of the
earth’s crust and cause a fault, i.e., cause the crust to
I When the plates move away from each other, the molten rupture and shift. When this occurs, it causes an
rock from the mantle fills the gaps between them to earthquake in the form of violent motion of the earth’s
form ocean basins. surface and/or large sea waves. Major earthquakes occur
2 While moving away from one plate, they will be moving because of this phenomenon.
closer to another and may collide. One plate may pile
up over the other and form mountains. Magnitude and quantum of energy released
3 If the plates pull down, they would sink into the mantle
and melt to form ocean basins. Some of the molten The magnitude of shocks and vibrations caused by an
rock of these plates may travel to the earth’s surface earthquake is the measure of energy released (E) at the
through the crevice so formed due to heat convection focal point in the form of seismic waves. It is measured
and cause a volcano. on a Richter scale. An American seismologist called