Page 464 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 464
14/438 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
- Eurasian date
,%Antarctic date /1 L
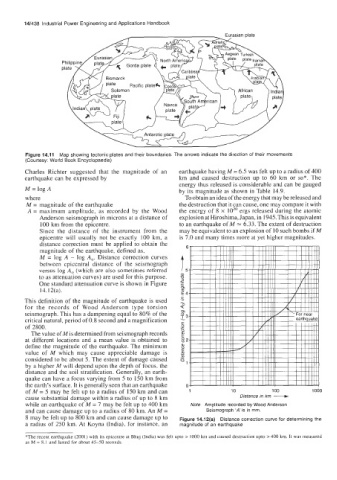
Figure 14.11 Map showing tectonic plates and their boundaries. The arrows indicate the direction of their movements
(Courtesy: World Book Encyclopaedia)
Charles Richter suggested that the magnitude of an earthquake having M = 6.5 was felt up to a radius of 400
earthquake can be expressed by km and caused destruction up to 60 km or so*. The
energy thus released is considerable and can be gauged
M = log A by its magnitude as shown in Table 14.9.
where To obtain an idea of the energy that may be released and
M = magnitude of the earthquake the destruction that it can cause, one may compare it with
A = maximum amplitude, as recorded by the Wood the energy of 8 x lo2" ergs released during the atomic
Anderson seismograph in microns at a distance of explosion at Hiroshima, Japan, in 1945. This is equivalent
100 km from the epicentre. to an earthquake of M = 6.33. The extent of destruction
Since the distance of the instrument from the may be equivalent to an explosion of 10 such bombs if M
epicentre will usually not be exactly 100 km, a is 7.0 and many times more at yet higher magnitudes.
distance correction must be applied to obtain the 6
magnitude of the earthquake, defined as,
versus log A, (which are also sometimes referred t,
M = log A - log A,. Distance correction curves
between cpiccntral distance of the seismograph
to as attenuation curves) are used for this purpose. 8
._
One standard attenuation curve is shown in Figure 2
14.12(a).
g4
This definition of the magnitude of earthquake is used .E
a
for the records of Wood Anderson type torsion T
01
seismograph. This has a dampening equal to 80% of the 8
critical natural, period of 0.8 second and a magnification L3
C
of 2800. .z
The value of M is determined from seismograph records 0
i?
at different locations and a mean value is obtained to 82
define the magnitude of the earthquake. The minimum 0
2
value of M which may cause appreciable damage is E
considered to be about 5. The extent of damage caused .Y
by a higher M will depend upon the depth of focus, the Q1
distance and the soil stratification. Generally, an earth-
quake can have a focus varying from 5 to 150 km from
the earth's surface. It is generally seen that an earthquake 0 Distance in km -
of M = 5 may be felt up to a radius of 150 km and can 1 10 100 1000
cause substantial damage within a radius of up to 8 km
while an earthquake of M = 7 may be felt up to 400 km Note Amplitude recorded by Wood Anderson
and can cause damage up to a radius of 80 km. An M = Seismograph 'A is in mm.
8 may be felt up to 800 km and can cause damage up to Figure 14.12(a) Distance correction curve for determining the
a radius of 250 km. At Koyna (India), for instance, an magnitude of an earthquake
*The recent earthquake (2001) with its epicentre at Bhuj (India) was felt upto > 1000 km and caused destruction upto > 400 km. It was measured
as M = 8.1 and lasted for about 45-50 seconds.