Page 832 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 832
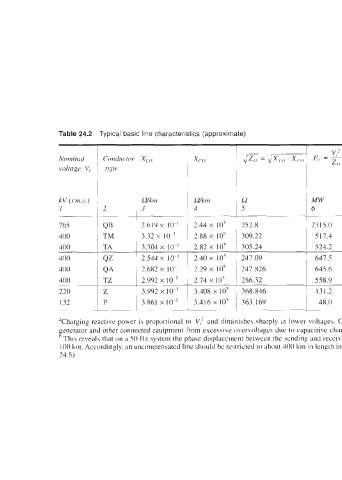
Table 24.2 Typical basic line characteristics (approximate)
~
I, (It Pi, Clia r,q ing ‘ Churgitzg ~ Ferrtrnti e8ec.t per km
- -5
--
-
0
17 Zn x<
LZkm ~ Wkrn I2 MW Amp Atrip ~ in rcrdintI.v In degree5
3 !4 5 6 7 8 9 ~ 10 11
~____~ ~- -
, ~ ~ ~ ~~~~
~
252.8 2315 0 1,747 I81 2.40 ~ 1.036 x IO-’ 59 33 x 10-3
309.22 SI7 4 747 0 80 0.56 1.074 x lo-’ 61 51 x IO ’
3.304 x IO-’ 2.82 x 10’ 305.24 524 2 757 0 82 0.567 1.082 x 1 of 61 97 x IO-’
2.544 x IO-’ 1 2.40 x 10’ 247.09 647 5 935 0 96 0.67 I .03 x I 0-1 58.99 x 10
645 6 932 IO1 0.70 I .082 x 10-3 61 97 x IO-’
558 9 807 0 84 0.584 1.045 x 10-3 59 85 x 10
220 2 3 992 x 10 I 1 3 408 x 10’ 368 846 131 2 344 0 31 0.142 1082 xIO-’ 61.97 x 10 ’
48 0 210 0 22 0 051 1 063 x 10 60.88 x 10 ’
__
~~ ~- ~~ _____
Tharging reactive power is proportional to V,’ and diminishes sharply at lower voltages. Charging reactive power mut be \uitably offset at the point of power generation to protect the
generator and other connected eauipment from excesive overvoltagcs due to capacitive charging.
This reveals that on a 50 Hz system the pha\e displacement between the sending and receiving end voltagca, due to electromaynctic propagation through the lines, is of the order of 6” per
100 km. Accordingly, an uncompensated line should be restricted to about 400 kin in length in radial lines and 800 km in symmetrical lines to avoid an overvoltage at the receiving end (Table
24.5)