Page 272 - Industrial Process Plant Construction Estimating and Man Hour Analysis
P. 272
Statistical applications to construction Chapter 12 251
12.6 Method of least squares for process piping
Example 12.6.1
Handle and install PVC pipe (Table 12.6.1)
Facility—Industrial plant
Data for input: Man-hours PVC piping
Man-hour (y): R 1 = 0.12, 0.12, 0.14, 0.18, 0.28, 0.37, 0.46, and 0.55
Pipe size, inches (x): R 2 = 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12
Man-hour per lineal feet
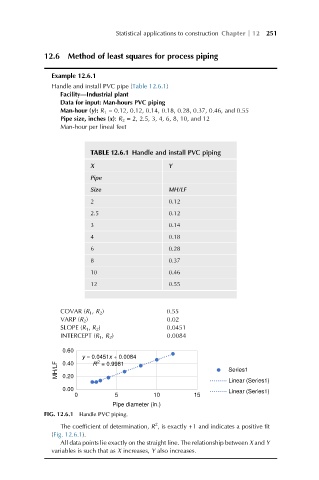
TABLE 12.6.1 Handle and install PVC piping
X Y
Pipe
Size MH/LF
2 0.12
2.5 0.12
3 0.14
4 0.18
6 0.28
8 0.37
10 0.46
12 0.55
COVAR (R 1 , R 2 ) 0.55
VARP (R 2 ) 0.02
SLOPE (R 1 , R 2 ) 0.0451
INTERCEPT (R 1 , R 2 ) 0.0084
0.60
y = 0.0451x + 0.0084
2
MH/LF R = 0.9981 Series1
0.40
0.20
Linear (Series1)
0.00 Linear (Series1)
0 5 10 15
Pipe diameter (in.)
FIG. 12.6.1 Handle PVC piping.
2
The coefficient of determination, R , is exactly +1 and indicates a positive fit
(Fig. 12.6.1).
All data points lie exactly on the straight line. The relationship between X and Y
variables is such that as X increases, Y also increases.