Page 409 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 409
An Introduction to Biological Treatment and Membrane Filtration 381
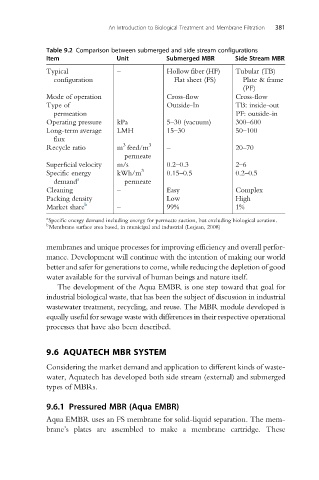
Table 9.2 Comparison between submerged and side stream configurations
Item Unit Submerged MBR Side Stream MBR
Typical – Hollow fiber (HF) Tubular (TB)
configuration Flat sheet (FS) Plate & frame
(PF)
Mode of operation Cross-flow Cross-flow
Type of Outside-In TB: inside-out
permeation PF: outside-in
Operating pressure kPa 5–30 (vacuum) 300–600
Long-term average LMH 15–30 50–100
flux
3
Recycle ratio m feed/m 3 – 20–70
permeate
Superficial velocity m/s 0.2–0.3 2–6
Specific energy kWh/m 3 0.15–0.5 0.2–0.5
demand a permeate
Cleaning – Easy Complex
Packing density Low High
Market share b – 99% 1%
a
Specific energy demand including energy for permeate suction, but excluding biological aeration.
b
Membrane surface area based, in municipal and industrial (Lesjean, 2008)
membranes and unique processes for improving efficiency and overall perfor-
mance. Development will continue with the intention of making our world
better and safer for generations to come, while reducing the depletion of good
water available for the survival of human beings and nature itself.
The development of the Aqua EMBR is one step toward that goal for
industrial biological waste, that has been the subject of discussion in industrial
wastewater treatment, recycling, and reuse. The MBR module developed is
equally useful for sewage waste with differences in their respective operational
processes that have also been described.
9.6 AQUATECH MBR SYSTEM
Considering the market demand and application to different kinds of waste-
water, Aquatech has developed both side stream (external) and submerged
types of MBRs.
9.6.1 Pressured MBR (Aqua EMBR)
Aqua EMBR uses an FS membrane for solid-liquid separation. The mem-
brane’s plates are assembled to make a membrane cartridge. These