Page 105 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 105
90 Measurement of level and volume
of a radio-frequency surface sensor to detect the
surface.
Self-balancing level sensors offer extreme
ranges, and variable forces exerted by changing
mechanical linkage geometry are made negligible.
Very high accuracies can be provided, the method
being virtually an automated tape measure.
5.5 Methods providing
short-range detection .....- .
p-----
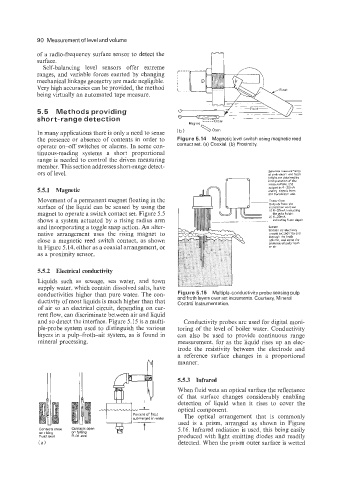
Magnet Close
In many applications there is only a need to sense (b) \Open
the presence or absence of contents in order to Figure 5.14 Magnetic level switch using magnetic reed
operate on-off switches or alarms. In some con- contact set. (a) Coaxial. (b) Proximity.
tinuous-reading systems a short proportional
range is needed to control the driven measuring
member. This section addresses short-range detect-
ors of level. Separate meawrernent3
of pulp depth and froth
m height are obtained by
mtermetation of the
measurement. and
5.5.1 Magnetic output 8s 4-20mA
the transmitter unit
Movement of a permanent magnet floating in the I IIII I- Transmitter
surface of the liquid can be sensed by using the OUtPUtE froin the
transmitter unit are
magnet to operate a switch contact set. Figure 5.5 1) the 4-20mA pulp heighT indicating
2) 4-20mA
shows a system actuated by a rising radius arm _-- mdicatmg froth depth
and incorporating a toggle snap action. An alter- Sensor
Sixteen condwtivitv
native arrangement uses the rising magnet to through the froth
prober extend into and
close a magnetic reed switch contact, as shown d~mn. and sense the
presence of pulp froth
in Figure 5.14, either as a coaxial arrangement, or o( air
as a proximity sensor.
5.5.2 Electrical conductivity
Liquids such as sewage, sea water, and town
supply water, which contain dissolved salts, have
conductivities higher than pure water. The con- Figure 5.15 Multiple-conductivity probesensing pulp
ductivity of most liquids is much higher than that and froth layers over set increments. Courtesy, Mineral
Control Instrumentation.
of air so an electrical circuit, depending on cur-
rent flow, can discriminate between air and liquid
and so detect the interface. Figure 5.15 is a multi- Conductivity probes are used for digital moni-
ple-probe system used to distinguish the various toring of the level of boiler water. Conductivity
layers in a pulp-froth-air system, as is found in can also be used to provide continuous range
mineral processing. measurement, for as the liquid rises up an elec-
trode the resistivity between the electrode and
a reference surface changes in a proportional
M manner.
5.5.3 Infrared
When fluid wets an optical surface the reflectance
of that surface changes considerably enabling
detection of liquid when it rises to cover the
optical component.
Percent of float The optical arrangement that is commonly
submerged in water
used is a prism, arranged as shown in Figure
contacts CIOEQ Contacts open 5.16. Infrared radiation is used, this being easily
on rising on falling
fluid level fluid ievei produced with light emitting diodes and readily
(a) detected. When the prism outer surface is wetted