Page 153 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 153
Pressure measurement 137
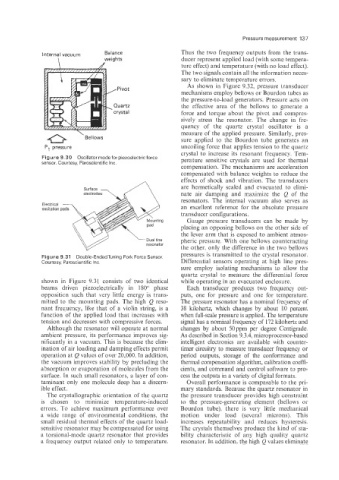
Internal vacuum Balance Thus the two frequency outputs from the trans-
\ weights ducer represent applied load (with some tempera-
ture effect) and temperature (with no load effect).
The two signals contain all the information neces-
sary to eliminate temperature errors.
As shown in Figure 9.32, pressure transducer
,Pivot
mechanisms employ bellows or Bourdon tubes as
the pressure-to-load generators. Pressure acts on
Quartz the effective area of the bellows to generate a
crystal force and torque about the pivot and compres-
sively stress the resonator. The change in fre-
quency of the quartz crystal oscillator is a
\ measure of the applied pressure. Similarly, pres-
Bellows sure applied to the Bourdon tube generates an
PI pressure uncoiling force that applies tension to the quartz
crystal to increase its resonant frequency. Tem-
Figure 9.30 Oscillator rnodefor piezoelectricforce perature sensitive crystals are used for thermal
sensor. Courtesy, Paroscientific Inc.
compensation. The mechanisms are acceleration
compensated with balance weights to reduce the
effects of shock and vibration. The transducers
are hermetically sealed and evacuated to elimi-
nate air damping and maximize the Q of the
resonators. The internal vacuum also serves as
an excellent reference for the absolute pressure
transducer configurations.
Gauge pressure transducers can be made by
placing an opposing bellows on the other side of
the lever arm that is exposed to ambient atrnos-
Dual
// - tine pheric pressure. With one bellows counteracting
the other, only the difference in the two bellows
Figure 9.31 Double-EndedTuning Fork Forcz Sensor. pressures is transmitted to the crystal resonator.
Courtesy, Paroscientific inc. Differential sensors operating at high line pres-
sure employ isolating mechanisms to allow the
quartz crystal to measure the differential force
shown in Figure 9.31 consists of two identical while operating in an evacuated enclosure.
beams driven piezoelectrically in 180" phase Each transducer produces two frequency out-
opposition such that very little energy is trans- puts, one for pressure and one for temperature.
mitted to the mounting pads. The high Q reso- The pressure resonator has a nominal frequency of
nant frequency, like that of a violin string, is a 38 kilohertz, which changes by about 10 percent
function of the applied load that increases with when full-scale pressure is applied. The temperature
tension and decreases with compressive forces. signal has a nominal frequency of 172 lcilohertz and
Although the resonator will operate at normal changes by about 50 ppm per degree Centigrade.
ambient pressure, its performance improves sig- As described in Section 9.3.4, microprocessor-based
nificantly in a vacuum. This is because the elim- intelligent electronics are available with counter-
ination of air loading and damping effects permit timer circuitry to measure transducer frequency or
operation at Q values of over 20,000. In addition, period outputs, storage of the conformance and
the vacuum improves stability by precluding the thermal compensation algorithm, calibration coeffi-
absorption or evaporation of molecules from the cients, and command and control software to pro-
surface. In such small resonators, a layer of con- cess the outputs in a variety of digital formats.
taminant only one molecule deep has a discern- Overall performance is comparable to the pri-
ible effect. mary standards. Because the quartz resonator in
The crystallographic orientation of the quartz the pressure transducer provides high constraint
is chosen to minimize temperature-induced to the pressure-generating element (bellows or
errors. To achieve maximum performance over Bourdon tube), there is very little mechanical
a wide range of environmental conditions, the motion under load (several microns). This
small residual thermal effects of the quartz load- increases repeatability and reduces hysteresis.
sensitive resonator may be compensated for using The crystals themselves produce the kind of sta-
a torsional-mode quartz resonator that provides bility characteristic of any high quality quartz
a frequency output related only to temperature. resonator. In addition, the high Q values eliminate