Page 264 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 264
242 C h a p t e r F o u r
Antenna Sum of Errors I
Height (m) a b G c Squared
5 1.15 -0 1 4 148.6 94.5 309
.
9 0 . 7 4 0.27 151.8 79.8 246
15 0.20 1.05 143.9 55.5 577
19 -0.48 2 . 36 158.3 37.3 296
TABLE 4.5.2.2.1 Results of Fitting the Proposed Propagation
Model to Experimental Results at 900 MHz Using a Least Squares
Regression Procedure
4.5.3 Physical Models
The empirical models in the previous section can provide reasonable results. However,
it is desirable to understand the physical mechanisms underlying them to gain insight
and to create physical models with potentially greater accuracy earlier. Depending on
the building distributions and antenna location and height, measurement data vary
drastically. This is one of the characteristics of microcell propagation.
3
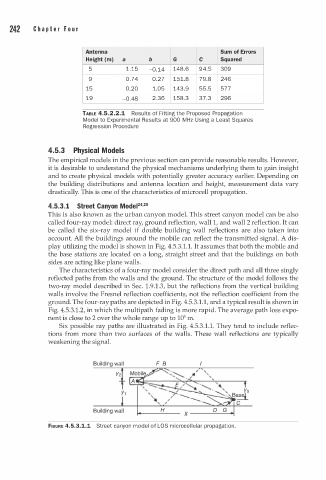
4.5. . 1 Street Canyon Model24·25
This is also known as the urban canyon model. This street canyon model can be also
called four-ray model: direct ray, ground reflection, wall 1, and wall 2 reflection. It can
be called the six-ray model if double building wall reflections are also taken into
account. All the buildings around the mobile can reflect the transmitted signal. A dis
play utilizing the model is shown in Fig. 4.5.3. . 1 . It assumes that both the mobile and
1
the base stations are located on a long, straight street and that the buildings on both
sides are acting like plane walls.
The characteristics of a four-ray model consider the direct path and all three singly
reflected paths from the walls and the ground. The structure of the model follows the
1
two-ray model described in Sec. . 9.1.3, but the reflections from the vertical building
walls involve the Fresnel reflection coefficients, not the reflection coefficient from the
ground. The four-ray paths are depicted in Fig. 4.5.3.1.1, and a typical result is shown in
Fig. 4.5.3.1.2, in which the multipath fading is more rapid. The average path loss expo
nent is close to 2 over the whole range up to 105 m.
Six possible ray paths are illustrated in Fig. 4.5. . 1 . 1 . They tend to include reflec
3
tions from more than two surfaces of the walls. These wall reflections are typically
weakening the signal.
Building wall F B
y�
Building wall
FIGURE 4.5.3.1.1 Street canyon model of LOS microc l l u l ar propagation.
e