Page 274 - Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
P. 274
P1: KsF/ICD
CB908/Date
0521853265c08
EXERCISES
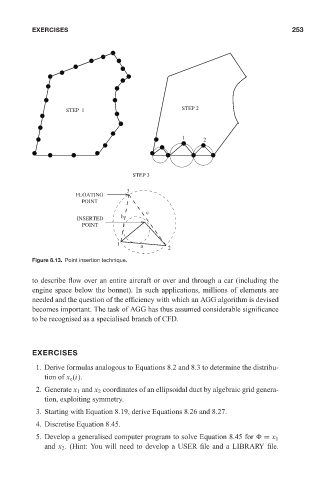
STEP 1 0 521 85326 5 STEP 2 May 10, 2005 16:28 253
1
2
STEP 3
3
FLOATING
POINT
c
INSERTED b
POINT
1 a 2
Figure 8.13. Point insertion technique.
to describe flow over an entire aircraft or over and through a car (including the
engine space below the bonnet). In such applications, millions of elements are
needed and the question of the efficiency with which an AGG algorithm is devised
becomes important. The task of AGG has thus assumed considerable significance
to be recognised as a specialised branch of CFD.
EXERCISES
1. Derive formulas analogous to Equations 8.2 and 8.3 to determine the distribu-
tion of x c (i).
2. Generate x 1 and x 2 coordinates of an ellipsoidal duct by algebraic grid genera-
tion, exploiting symmetry.
3. Starting with Equation 8.19, derive Equations 8.26 and 8.27.
4. Discretise Equation 8.45.
5. Develop a generalised computer program to solve Equation 8.45 for = x 1
and x 2 . (Hint: You will need to develop a USER file and a LIBRARY file.