Page 163 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 163
146 J. MILSOM
In-phase
(dip angle)
Quadrature
To transmitter
E
Secondary
field
Dip angle H
Dip angle
Power
Secondary Secondary
Primary Primary
Primary
Magnetic
Field
Secondary
magnetic field
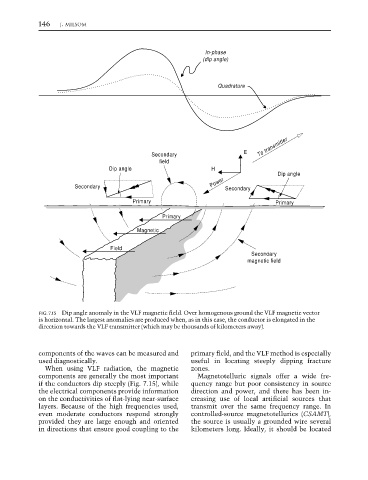
FIG. 7.15 Dip angle anomaly in the VLF magnetic field. Over homogenous ground the VLF magnetic vector
is horizontal. The largest anomalies are produced when, as in this case, the conductor is elongated in the
direction towards the VLF transmitter (which may be thousands of kilometers away).
components of the waves can be measured and primary field, and the VLF method is especially
used diagnostically. useful in locating steeply dipping fracture
When using VLF radiation, the magnetic zones.
components are generally the most important Magnetotelluric signals offer a wide fre-
if the conductors dip steeply (Fig. 7.15), while quency range but poor consistency in source
the electrical components provide information direction and power, and there has been in-
on the conductivities of flat-lying near-surface creasing use of local artificial sources that
layers. Because of the high frequencies used, transmit over the same frequency range. In
even moderate conductors respond strongly controlled-source magnetotellurics (CSAMT),
provided they are large enough and oriented the source is usually a grounded wire several
in directions that ensure good coupling to the kilometers long. Ideally, it should be located