Page 292 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 292
Bipolar Technology 271
n buried layer (sub-collector)
+
p-substrate + + p-base +
p n p
+
(a) n buried layer (sub-collector)
p-substrate
n-epilayer
n buried layer (sub-collector)
+
(d)
p-substrate
(b)
n p
+
+
+
p guard n contact p guard p + n + p +
ring
+
n buried layer (sub-collector)
n-epi
p-substrate
+
n buried layer (sub-collector)
p-substrate
(e)
(c)
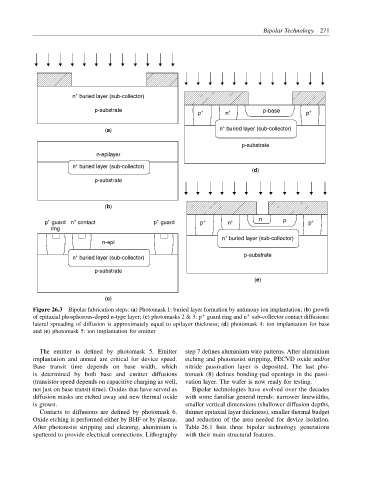
Figure 26.3 Bipolar fabrication steps: (a) Photomask 1: buried layer formation by antimony ion implantation; (b) growth
+
+
of epitaxial phosphorous-doped n-type layer; (c) photomasks 2 & 3: p guard ring and n sub-collector contact diffusions:
lateral spreading of diffusion is approximately equal to epilayer thickness; (d) photomask 4: ion implantation for base
and (e) photomask 5: ion implantation for emitter
The emitter is defined by photomask 5. Emitter step 7 defines aluminium wire patterns. After aluminium
implantation and anneal are critical for device speed. etching and photoresist stripping, PECVD oxide and/or
Base transit time depends on base width, which nitride passivation layer is deposited. The last pho-
is determined by both base and emitter diffusions tomask (8) defines bonding-pad openings in the passi-
(transistor speed depends on capacitive charging as well, vation layer. The wafer is now ready for testing.
not just on base transit time). Oxides that have served as Bipolar technologies have evolved over the decades
diffusion masks are etched away and new thermal oxide with some familiar general trends: narrower linewidths,
is grown. smaller vertical dimensions (shallower diffusion depths,
Contacts to diffusions are defined by photomask 6. thinner epitaxial layer thickness), smaller thermal budget
Oxide etching is performed either by BHF or by plasma. and reduction of the area needed for device isolation.
After photoresist stripping and cleaning, aluminium is Table 26.1 lists three bipolar technology generations
sputtered to provide electrical connections. Lithography with their main structural features.