Page 354 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 354
Tools for CVD and Epitaxy 333
MOCVD has also been studied for metal deposition. as metal organics. Many MOs are extremely reactive
Copper has been deposited from precursors such with oxygen, and premature contact with oxygen will
as vinyltrimethylsilane hexafluoroacetylacetonate, destroy the precursors.
VTMSCu(hfac), or Cu(I)-β-diketonate. Conformal depo-
sition is possible and filling of high aspect ratio holes has 33.5 SILICON CVD EPITAXY
been demonstrated. Trimethyl aluminium source gas has
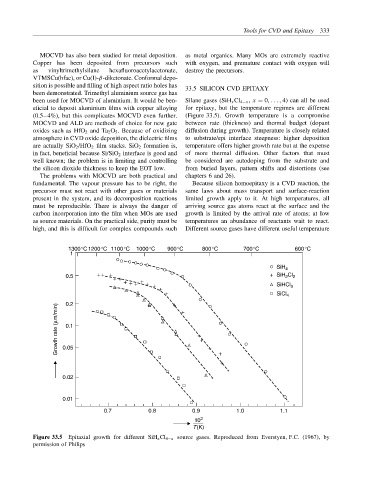
been used for MOCVD of aluminium. It would be ben- Silane gases (SiH x Cl 4−x , x = 0, . . . , 4) can all be used
eficial to deposit aluminium films with copper alloying for epitaxy, but the temperature regimes are different
(0.5–4%), but this complicates MOCVD even further. (Figure 33.5). Growth temperature is a compromise
MOCVD and ALD are methods of choice for new gate between rate (thickness) and thermal budget (dopant
oxides such as HfO 2 and Ta 2 O 5 . Because of oxidizing diffusion during growth). Temperature is closely related
atmosphere in CVD oxide deposition, the dielectric films to substrate/epi interface steepness: higher deposition
are actually SiO 2 /HfO 2 film stacks. SiO 2 formation is, temperature offers higher growth rate but at the expense
in fact, beneficial because Si/SiO 2 interface is good and of more thermal diffusion. Other factors that must
well known; the problem is in limiting and controlling be considered are autodoping from the substrate and
the silicon dioxide thickness to keep the EOT low. from buried layers, pattern shifts and distortions (see
The problems with MOCVD are both practical and chapters 6 and 26).
fundamental. The vapour pressure has to be right, the Because silicon homoepitaxy is a CVD reaction, the
precursor must not react with other gases or materials same laws about mass transport and surface-reaction
present in the system, and its decomposition reactions limited growth apply to it. At high temperatures, all
must be reproducible. There is always the danger of arriving source gas atoms react at the surface and the
carbon incorporation into the film when MOs are used growth is limited by the arrival rate of atoms; at low
as source materials. On the practical side, purity must be temperatures an abundance of reactants wait to react.
high, and this is difficult for complex compounds such Different source gases have different useful temperature
1300°C 1200°C 1100°C 1000°C 900°C 800°C 700°C 600°C
1
SiH 4
0.5 + + + + SiH Cl 2
2
+ +
+ + + + + + SiHCl 3
+
+ + SiCl 4
0.2
Growth rate (µm/min) 0.1 + + +
0.05
+
+
+
0.02
0.01
0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1
10 3
T(K)
Figure 33.5 Epitaxial growth for different SiH x Cl 4−x source gases. Reproduced from Everstyen, F.C. (1967), by
permission of Philips