Page 81 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 81
60 Introduction to Microfabrication
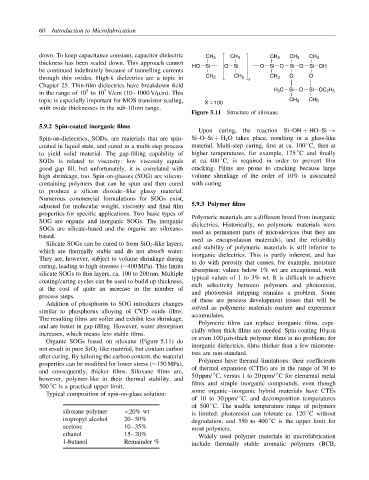
down. To keep capacitance constant, capacitor dielectric CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
thickness has been scaled down. This approach cannot HO Si O Si O Si O Si O Si OH
be continued indefinitely because of tunnelling currents
through thin oxides. High-k dielectrics are a topic in CH 3 CH 3 x CH 3 O O
Chapter 25. Thin-film dielectrics have breakdown field H 3 C Si O
5
7
in the range of 10 to 10 V/cm (10–1000 V/µm). This Si OC 2 H 5
topic is especially important for MOS transistor scaling, X 100 CH 3 CH 3
~
~
with oxide thicknesses in the sub-10 nm range.
Figure 5.11 Structure of siloxane
5.9.2 Spin-coated inorganic films
Upon curing, the reaction Si–OH + HO–Si →
Spin-on-dielectrics, SODs, are materials that are spin- Si–O–Si + H 2 O takes place, resulting in a glass-like
◦
coated in liquid state, and cured in a multi-step process material. Multi-step curing, first at ca. 100 C, then at
◦
to yield solid material. The gap-filling capability of higher temperatures, for example, 175 C and finally
◦
SODs is related to viscosity: low viscosity equals at ca. 400 C, is required in order to prevent film
good gap fill, but unfortunately, it is correlated with cracking. Films are prone to cracking because large
high shrinkage, too. Spin-on-glasses (SOG) are silicon- volume shrinkage of the order of 10% is associated
containing polymers that can be spun and then cured with curing.
to produce a silicon dioxide–like glassy material.
Numerous commercial formulations for SOGs exist,
adjusted for molecular weight, viscosity and final film 5.9.3 Polymer films
properties for specific applications. Two basic types of Polymeric materials are a different breed from inorganic
SOG are organic and inorganic SOGs. The inorganic dielectrics. Historically, no polymeric materials were
SOGs are silicate-based and the organic are siloxane- used as permanent parts of microdevices (but they are
based. used as encapsulation materials), and the reliability
Silicate SOGs can be cured to form SiO 2 -like layers,
and stability of polymeric materials is still inferior to
which are thermally stable and do not absorb water.
inorganic dielectrics. This is partly inherent, and has
They are, however, subject to volume shrinkage during
curing, leading to high stresses (∼400 MPa). This limits to do with porosity that causes, for example, moisture
silicate SOGs to thin layers, ca. 100 to 200 nm. Multiple absorption: values below 1% wt are exceptional, with
coating/curing cycles can be used to build up thickness, typical values of 1 to 3% wt. It is difficult to achieve
etch selectivity between polymers and photoresist,
at the cost of quite an increase in the number of and photoresist stripping remains a problem. Some
process steps. of these are process development issues that will be
Addition of phosphorus to SOG introduces changes
similar to phosphorus alloying of CVD oxide films. solved as polymeric materials mature and experience
accumulates.
The resulting films are softer and exhibit less shrinkage,
Polymeric films can replace inorganic films, espe-
and are better in gap filling. However, water absorption
increases, which means less stable films. cially when thick films are needed. Spin coating 10 µm
Organic SOGs based on siloxane (Figure 5.11) do or even 100 µm-thick polymer films is no problem; for
not result in pure SiO 2 -like material, but contain carbon inorganic dielectrics, films thicker than a few microme-
after curing. By tailoring the carbon content, the material tres are non-standard.
properties can be modified for lower stress (∼150 MPa), Polymers have thermal limitations: their coefficients
and consequently, thicker films. Siloxane films are, of thermal expansion (CTEs) are in the range of 30 to
◦
◦
however, polymer-like in their thermal stability, and 50 ppm/ C, versus 1 to 20 ppm/ C for elemental metal
◦
500 C is a practical upper limit. films and simple inorganic compounds, even though
some organic–inorganic hybrid materials have CTEs
Typical composition of spin-on-glass solution:
◦
of 10 to 30 ppm/ C, and decomposition temperatures
◦
of 500 C. The usable temperature range of polymers
siloxane polymer <20% wt is limited: photoresist can tolerate ca. 120 C without
◦
isopropyl alcohol 20–50% degradation, and 350 to 400 C is the upper limit for
◦
acetone 10–35% most polymers.
ethanol 15–20% Widely used polymer materials in microfabrication
1-butanol Remainder % include thermally stable aromatic polymers (BCB,