Page 274 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 274
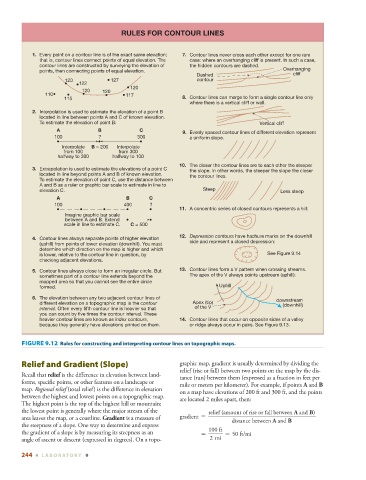
RULES FOR CONTOUR LINES
1. Every point on a contour line is of the exact same elevation; 7. Contour lines never cross each other except for one rare
that is, contour lines connect points of equal elevation. The case: where an overhanging cliff is present. In such a case,
contour lines are constructed by surveying the elevation of the hidden contours are dashed.
points, then connecting points of equal elevation. Overhanging
Dashed cliff
120 127 contour
122
120
120 120
110 117
115 8. Contour lines can merge to form a single contour line only
where there is a vertical cliff or wall.
2. Interpolation is used to estimate the elevation of a point B
located in line between points A and C of known elevation.
To estimate the elevation of point B: Vertical cliff
A B C
9. Evenly spaced contour lines of different elevation represent
100 ? 300 a uniform slope.
Interpolate B = 200 Interpolate
from 100 from 300
halfway to 300 halfway to 100
10. The closer the contour lines are to each other the steeper
3. Extrapolation is used to estimate the elevations of a point C the slope. In other words, the steeper the slope the closer
located in line beyond points A and B of known elevation. the contour lines.
To estimate the elevation of point C, use the distance between
A and B as a ruler or graphic bar scale to estimate in line to
elevation C. Steep Less steep
A B C
100 400 ?
11. A concentric series of closed contours represents a hill:
Imagine graphic bar scale
between A and B. Extend
scale in line to estimate C. C = 500
12. Depression contours have hachure marks on the downhill
4. Contour lines always separate points of higher elevation
side and represent a closed depression:
(uphill) from points of lower elevation (downhill). You must
determine which direction on the map is higher and which
is lower, relative to the contour line in question, by See Figure 9.14
checking adjacent elevations.
5. Contour lines always close to form an irregular circle. But 13. Contour lines form a V pattern when crossing streams.
sometimes part of a contour line extends beyond the The apex of the V always points upstream (uphill):
mapped area so that you cannot see the entire circle
formed. Uphill
6. The elevation between any two adjacent contour lines of downstream
different elevation on a topographic map is the contour Apex (tip) (downhill)
interval. Often every fifth contour line is heavier so that of the V
you can count by five times the contour interval. These
heavier contour lines are known as index contours, 14. Contour lines that occur on opposite sides of a valley
because they generally have elevations printed on them. or ridge always occur in pairs. See Figure 9.13.
FIGURE 9.12 Rules for constructing and interpreting contour lines on topographic maps.
Relief and Gradient (Slope) graphic map, gradient is usually determined by dividing the
relief (rise or fall) between two points on the map by the dis-
Recall that relief is the difference in elevation between land-
tance (run) between them (expressed as a fraction in feet per
forms, specific points, or other features on a landscape or
mile or meters per kilometer). For example, if points A and B
map. Regional relief (total relief) is the difference in elevation
on a map have elevations of 200 ft and 300 ft, and the points
between the highest and lowest points on a topographic map.
are located 2 miles apart, then:
The highest point is the top of the highest hill or mountain;
the lowest point is generally where the major stream of the relief (amount of rise or fall between A and B)
area leaves the map, or a coastline. Gradient is a measure of gradient =
distance between A and B
the steepness of a slope. One way to determine and express
100 ft
the gradient of a slope is by measuring its steepness as an = = 50 ft/mi
angle of ascent or descent (expressed in degrees). On a topo- 2 mi
244 ■ L ABOR ATORY 9