Page 247 - MEMS Mechanical Sensors
P. 247
236 Flow Sensors
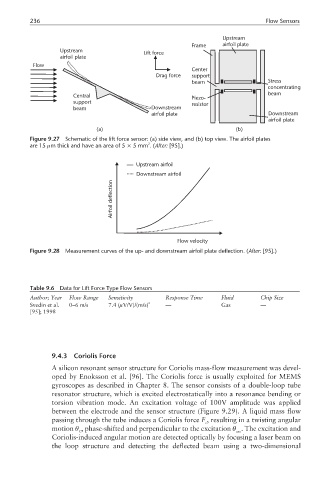
Upstream
Frame airfoil plate
Upstream Lift force
airfoil plate
Flow
Center
Drag force support
beam Stress
concentrating
Central Piezo- beam
support resistor
beam Downstream
airfoil plate Downstream
airfoil plate
(a) (b)
Figure 9.27 Schematic of the lift force sensor: (a) side view, and (b) top view. The airfoil plates
2
are 15 µm thick and have an area of 5 × 5mm .(After: [95].)
Upstream airfoil
Downstream airfoil
deflection
Airfoil
Flow velocity
Figure 9.28 Measurement curves of the up- and downstream airfoil plate deflection. (After: [95].)
Table 9.6 Data for Lift Force Type Flow Sensors
Author; Year Flow Range Sensitivity Response Time Fluid Chip Size
Svedin et al. 0–6 m/s 7.4 (µV/V)/(m/s) 2 — Gas —
[95]; 1998
9.4.3 Coriolis Force
A silicon resonant sensor structure for Coriolis mass-flow measurement was devel-
oped by Enoksson et al. [96]. The Coriolis force is usually exploited for MEMS
gyroscopes as described in Chapter 8. The sensor consists of a double-loop tube
resonator structure, which is excited electrostatically into a resonance bending or
torsion vibration mode. An excitation voltage of 100V amplitude was applied
between the electrode and the sensor structure (Figure 9.29). A liquid mass flow
passing through the tube induces a Coriolis force F , resulting in a twisting angular
c
motion θ , phase-shifted and perpendicular to the excitation θ . The excitation and
C exc
Coriolis-induced angular motion are detected optically by focusing a laser beam on
the loop structure and detecting the deflected beam using a two-dimensional