Page 689 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 689
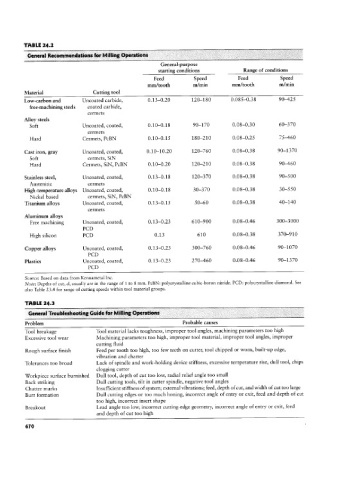
TABLE 24.2
General Recommendations fur Milling Operations
General-purpose
starting conditions Range of conditions
Feed Speed Feed Speed
mm/tooth m/min mm/tooth m/min
Material Cutting tool
Low-carbon and Uncoated carbide, 0.13-0.20 120-180 0.085-0.38 90-425
free-machining steels coated carbide,
cermets
Alloy steels
Soft Uncoated, coated, 0.10-0.18 90-170 0.08-0.30 60-370
cermets
Hard Cermets, PCBN 0.10-0.15 180-210 0.08-0.25 75-460
Cast iron, gray Uncoated, coated, 0.10-10.20 120-760 0.08-0.38 90-1370
Soft cermets, SiN
Hard Cerrnets, SiN, PCBN 0.10-0.20 120-210 0.08-0.38 90-460
Stainless steel, Uncoated, coated, 0.13-0.18 120-370 0.08-0.38 90-500
Austenitic cermets
High-temperature alloys Uncoated, coated, 0.10-0.1 8 30-370 0.08-0.38 30-550
Nickel based cermets, SiN, PCBN
Titanium alloys Uncoated, coated, 0.13-0.15 50-60 0.08-0.38 40-140
cermets
Aluminum alloys
Free machining Uncoated, coated, 0.13-0.23 610-900 0.08-0.46 300-3000
PCD
High silicon PCD 0.13 610 0.08-0.38 370-910
Copper alloys Uncoated, coated, 0.13-0.23 300-760 0.08-0.46 90-1070
PCD
Plastics Uncoated, coated, 0.13-0.23 270-460 0.08-0.46 90-1370
PCD
Source: Based on data from Kennametal Inc.
Note: Depths of cut, d, usually are in the range of 1 to 8 rnm. PcBN: polycrystalline cubic-boron nitride. PCD: polycrystalline diamond. See
also Table 23.4 for range of cutting speeds within tool material groups.
TABLE 24.3
General Troubleshooting Guide for Milling Qperations
Problem Probable causes
Tool breakage Tool material lacks toughness, improper tool angles, machining parameters too high
Excessive tool wear Machining parameters too high, improper tool material, improper tool angles, improper
cutting fluid
Rough surface finish Feed per tooth too high, too few teeth on cutter, tool chipped or worn, built-up edge,
vibration and chatter
Tolerances too broad Lack of spindle and work-holding device stiffness, excessive temperature rise, dull tool, chips
clogging cutter
Workpiece surface burnished Dull tool, depth of cut too low, radial relief angle too small
Back striking Dull cutting tools, tilt in cutter spindle, negative tool angles
Chatter marks Insufficient stiffness of system; external vibrations; feed, depth of cut, and width of cut too large
Burr formation Dull cutting edges or too much honing, incorrect angle of entry or exit, feed and depth of cut
too high, incorrect insert shape
Breakout Lead angle too low, incorrect cutting-edge geometry, incorrect angle of entry or exit, feed
and depth of cut too high
670