Page 346 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 346
318 • Chapter 9 / Phase Diagrams
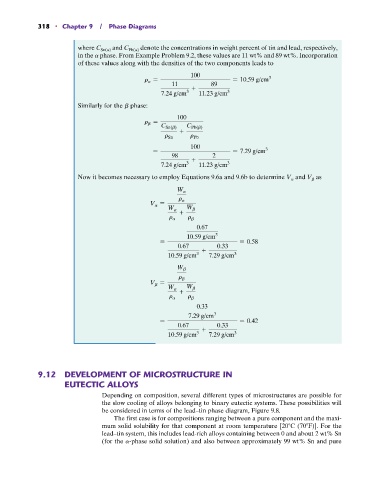
where C Sn(a) and C Pb(a) denote the concentrations in weight percent of tin and lead, respectively,
in the a phase. From Example Problem 9.2, these values are 11 wt% and 89 wt%. Incorporation
of these values along with the densities of the two components leads to
100
r a = = 10.59 g/cm 3
11 89
+ 3
3
7.24 g/cm 11.23 g/cm
Similarly for the b phase:
100
r b =
C Sn(b) C Pb(b)
+
r Sn r Pb
100 3
= = 7.29 g/cm
98 2
+
7.24 g/cm 3 11.23 g/cm 3
Now it becomes necessary to employ Equations 9.6a and 9.6b to determine V a and V b as
W a
r a
V a =
W a W b
+
r a r b
0.67
10.59 g/cm 3
= = 0.58
0.67 0.33
+
10.59 g/cm 3 7.29 g/cm 3
W b
r b
V b =
W a W b
+
r a r b
0.33
7.29 g/cm 3
= = 0.42
0.67 0.33
+ 3
3
10.59 g/cm 7.29 g/cm
9.12 DEVELOPMENT OF MICROSTRUCTURE IN
EUTECTIC ALLOYS
Depending on composition, several different types of microstructures are possible for
the slow cooling of alloys belonging to binary eutectic systems. These possibilities will
be considered in terms of the lead–tin phase diagram, Figure 9.8.
The first case is for compositions ranging between a pure component and the maxi-
mum solid solubility for that component at room temperature [20 C (70 F)]. For the
lead–tin system, this includes lead-rich alloys containing between 0 and about 2 wt% Sn
(for the a-phase solid solution) and also between approximately 99 wt% Sn and pure