Page 401 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 401
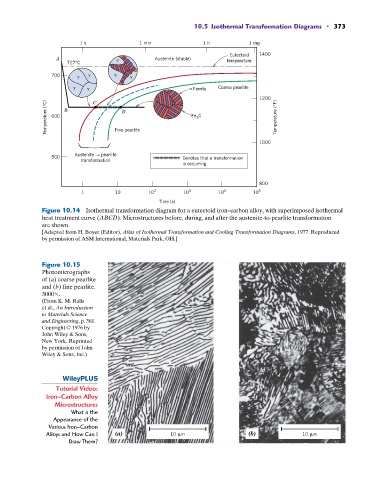
10.5 Isothermal Transformation Diagrams • 373
1 s 1 min 1 h 1 day
Eutectoid 1400
A Austenite (stable) temperature
727°C
700
Ferrite Coarse pearlite
1200
Temperature (°C) 600 B Fine pearlite Fe C Temperature (°F)
C
D
3
1000
Austenite → pearlite
500 Denotes that a transformation
transformation
is occurring
800
1 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5
Time (s)
Figure 10.14 Isothermal transformation diagram for a eutectoid iron–carbon alloy, with superimposed isothermal
heat treatment curve (ABCD). Microstructures before, during, and after the austenite-to-pearlite transformation
are shown.
[Adapted from H. Boyer (Editor), Atlas of Isothermal Transformation and Cooling Transformation Diagrams, 1977. Reproduced
by permission of ASM International, Materials Park, OH.]
Figure 10.15
Photomicrographs
of (a) coarse pearlite
and (b) fine pearlite.
3000 .
(From K. M. Ralls
et al., An Introduction
to Materials Science
and Engineering, p. 361.
Copyright © 1976 by
John Wiley & Sons,
New York. Reprinted
by permission of John
Wiley & Sons, Inc.)
Tutorial Video:
Iron–Carbon Alloy
Microstructures
What is the
Appearance of the
Various Iron–Carbon
Alloys and How Can I (a) 10 m (b) 10 m
Draw Them?